Vector Fonts
Overview
The MicroVG library enables the usage of Vector Fonts.
Compared to MicroUI Fonts, Vector Fonts brings the following features:
the text strings are scalable and can be transformed using a Matrix object.
the TTF/OTF font files don’t need to be preprocessed.
the text strings can be drawn with opacity, a color or a linear gradient.
The library also considers the Kerning space described in the font file kerning table, and allows a fine adjustement of the inter-letters spacing.
It also provides metrics measurement methods to correctly place the text within the surrounding drawing elements (i.e. in a label).
Loading a Font File
A Vector Font has to be loaded in a VectorFont object with a call to ej.microvg.VectorFont.loadFont(). This VectorFont object can then be used to draw text strings.
The fonts are decoded at runtime.
They don’t need to be pre-processed by some generator tool like MicroUI Fonts
Vector Font files must be declared as resources in a .resources.list file available in the classpath (Application Resources).
To declare them as external resources, the font files must be declared too in a .externresources.list file.
Text String Drawing
A string can be drawn in the graphics context with a call to ej.microvg.VectorGraphicsPainter.drawString().
The text string height is scalable, and multiple font files can be used in parrallel.
Text Color
The text string can be colored with the graphics context color or a with a linear gradient(Linear Gradient).
FillType and Alpha Blending Mode are also managed similarly to Path drawing (refer to Fill Type and Opacity and Blending Mode).
Text Transformations
The text string can also be transformed with a Matrix to translate, rotate, scale the drawing.
Letter Spacing
The inter character distance can be adjusted for each string drawing. By default, the inter character distance is computed from the font file metrics, considering kerning, if the font file includes a kerning table. It can be adjusted with the letterSpacing parameter of drawString(). Its default value is 0 pixel, a positive/negative value will increase/reduce the inter space distance by the corresponding pixel value.
Colored Emojis
The library supports the drawing of colored multilayer glyphs, but only for the embedded implementation. The simulator implementation draws the full emoji glyph with the color of the graphics context.
Only font files with CPAL/COLR tables are supported.
Font files with CBDT/CBLC tables are not supported.
To add colored emojis to a font, see the tutorial How to Add Emojis to a Vector Font.
Metrics and Text Positioning
All metrics provided by the ej.microvg.VectorFont class are given for a specific font size. The font size defines the height to which each character bounding box will be scaled.
The following figure presents some concepts of font metrics standarts:
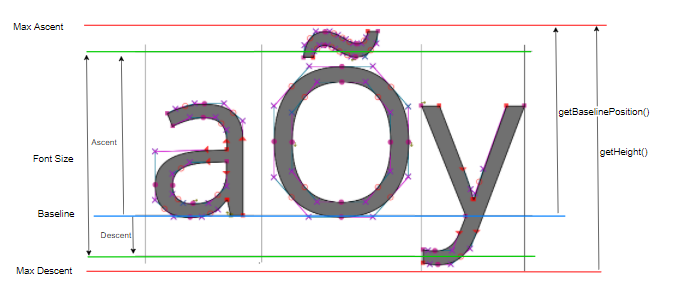
When a string is drawn with a call to ej.microvg.VectorGraphicsPainter.drawString() or ej.microvg.VectorGraphicsPainter.drawGradientString(), the anchor point of the string is the top left corner of the text rendering box. This anchor point is located horizontally on the first pixel of the first drawn glyph and vertically on the max ascent line.
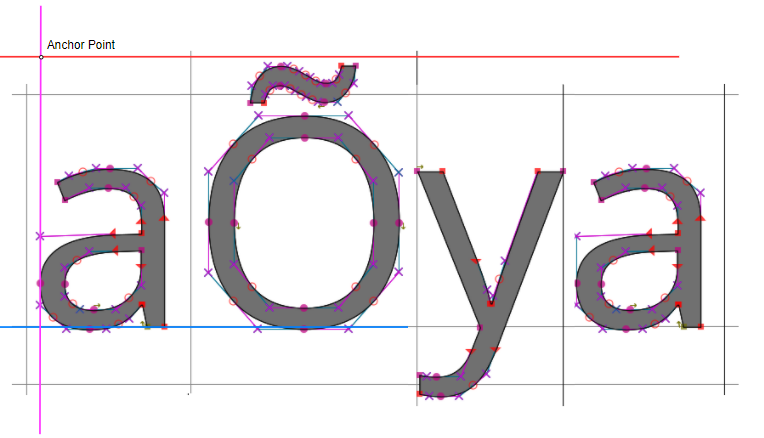
The ej.microvg.VectorFont.getBaselinePosition() method can be used to position the text baseline on a horizontal line.
The ej.microvg.VectorFont.getHeight() method can be used to center a text inside a label, by positionning the anchor point in order to have the same space above and below the text string.
Two other methods are available to position a known text in a label:
These methods return the width and height of a string drawing. They are computed from the width and height of the glyphs composing the string.
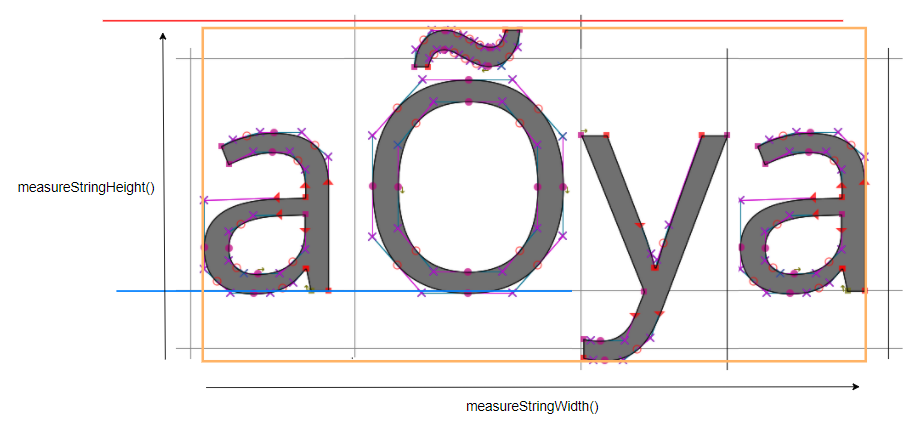
These methods can measure a specific glyph width and height using a one character string.
Note
The metrics are extracted from the character glyph metrics without considering the antialiasing introduced by the glyphs rasterizer.
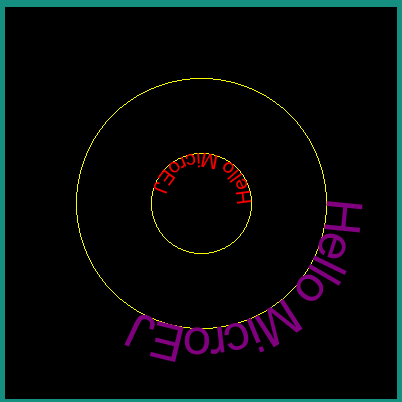
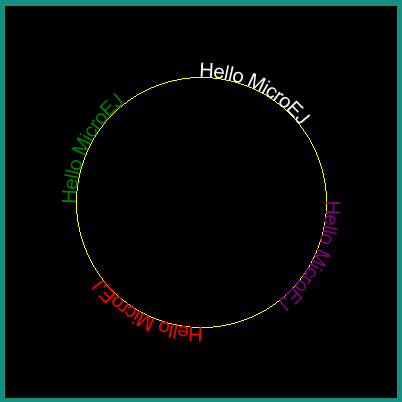
Drawing a Text on a Circle
The library proposes the drawing of a text on a circle by a call to ej.microvg.VectorGraphicsPainter.drawStringOnCircle(). The string is rendered as if the baseline of the string was a circle arc.
The string direction can be either clockwise or counter clockwise.
All the features described above are still available (linear gradient, transformations, letter spacing, kerning, colored emojis).
The anchor point of the drawing is the center of the circle.
The position where the text starts along the circle is the 3 o’clock position (positive X axis). This starting position can be modified by specifying a rotation into the transformation Matrix.
Complex Text Layout
Some scripts like Arabic or Thai scripts request a specific text layout mode where the shape or positioning of a grapheme depends on its relation to other graphemes (Refer to https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Complex_text_layout).
The MicroVG library provides two different layout modes:
the simple layout mode for latin scripts and other scripts where character unicodes and glyphs are one-to-one associated.
the complex layout mode for complex text layout scripts like arabic or thai.
The simple layout mode draws the text character as described in the previous sections. It uses the font Kerning table and the glyphs advanceX parameter to position the glyphs one after the other.
The complex layout mode uses the GPOS and GSUB font tables to substitute and position the character glyph.
The complex layout mode can be selected while loading the glyph with ej.microvg.VectorFont.loadFont by passing a supplementary boolean argument with value true.
Next example shows the same arabic string drawn with the same font but with simple (in white) and complex layout(in RED).
Text Measurement and Positioning
The measurement of string in complex layout mode respects the requirements presented in Metrics and Text Positioning.
Strings from script where text is read from right to left, like arabic, are still drawn with the anchor point located on the top left of the string.
Bidirectional Text
The complex layout mode does not support bidirectional text. A bidirectional text has to be splitted in multiple strings and each string has to be drawn to the correct location.
Limitations
The simulator rendering of complex layout mode for Drawing a Text on a Circle feature is done with many approximations. This rendering can still be used to have an overview of the text positionning on the display.
The letterSpacing feature is not supported by the simulator implementation. Texts will be displayed with a letterspacing value of 0.
External Fonts
To fetch fonts from external memory, the application must pre-register the external Font resources. The management of this kind of font may be different than the internal images and may require some allocations in the runtime memory. For more details about the external font management, refers to the VEE Port Guide chapter External Memory.