C Modules
Principle
Several C modules implement the UI Pack’s Abstraction Layer APIs. Some are generic, and some are VEE Port dependent (more precisely: GPU-dependent). The generic modules provide header files to be implemented by the specific modules. The generic C modules are available on the Central Repository and the specific C modules on the Developer Repository.
The picture below illustrates the available C modules, and the following chapters explain the aim and relations of each C module.
Note
It is a simplified view: all sources and header files of each C module are not visible.
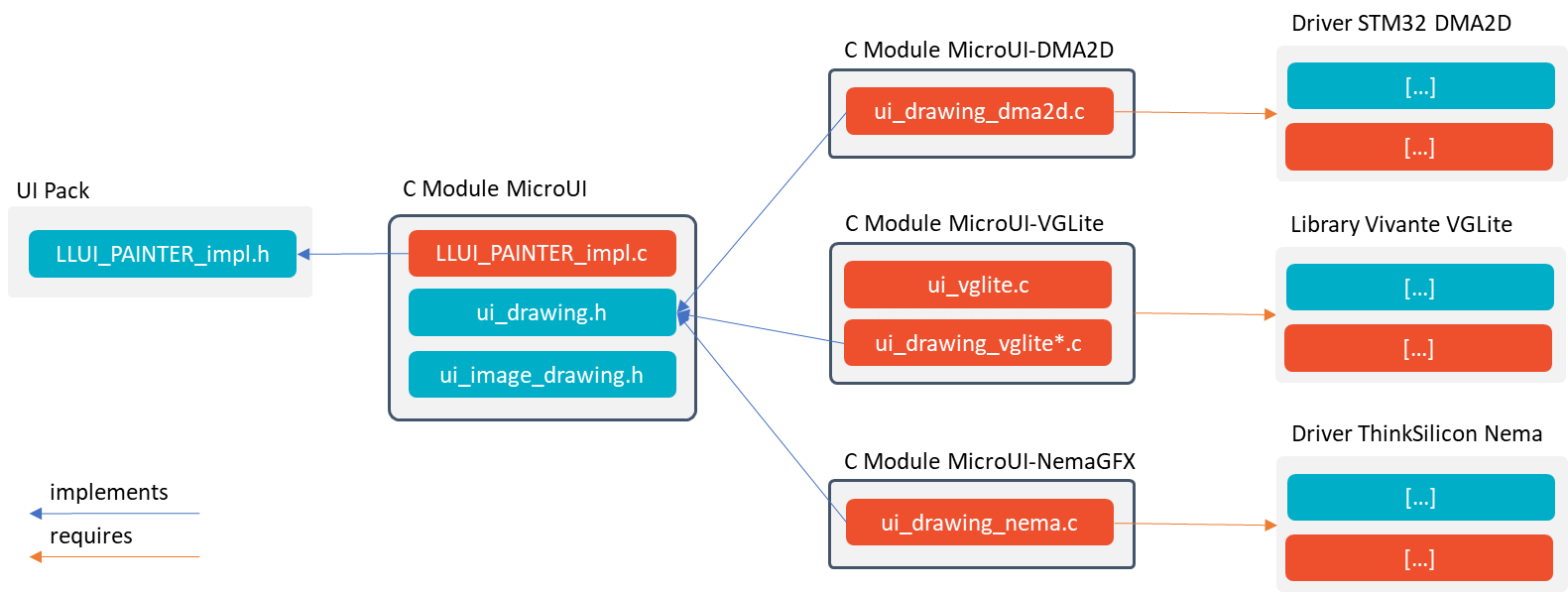
MicroUI C Modules
UI Pack
The UI Pack provides a header file to implement the MicroUI drawings: LLUI_PAINTER_impl.h.
See the UI Pack chapter to have more information.
The UI Pack and its header files are available on the Central Repository: https://repository.microej.com/modules/com/microej/pack/ui/ui-pack/.
C Module: MicroUI
This C module is divided into several parts, and each part provides an implementation of some MicroUI Abstraction Layer APIs. This C module is mandatory to use the UI Pack (the C files must be compiled in the BSP), but some C files are optional.
This C module is available on the Central Repository: com.microej.clibrary.llimpl#microui.
Drawings
Overview
This part aims to facilitate the MicroUI Painter classes implementation:
It manages the synchronization with the Graphics Engine (see
LLUI_DISPLAY_requestDrawing()).It checks the drawing parameters: clip, opacity, thickness, fade, image status, etc.
It logs the drawings (see Debug Traces).
It deports the rendering to
ui_drawing.h.
The implementation of ui_drawing.h depends on several options:
Whether the BSP provides a renderer (software and / or hardware as a GPU),
Whether the BSP is configured to handle several destination formats,
Whether the BSP is configured to handle custom image formats.
Files
Implements:
LLUI_PAINTER_impl.handLLDW_PAINTER_impl.h.C files:
LLUI_PAINTER_impl.c,LLDW_PAINTER_impl.c,ui_drawing_stub.c,ui_drawing.candui_image_drawing.c.Status: mandatory.
Usage
Add all C files in the BSP project.
Check the port by running the
uivalidation as described in the VEE Port project template
Images Heap
Overview
This part is optional since the MicroUI Graphics Engine already includes an Images Heap allocator. Like MicroUI Graphics Engine’s images heap allocator, the C module’s images allocator is a best-fit allocator. This kind of allocator has the following constraints:
It requires a header at the beginning of the heap section.
It adds a header and a footer for each allocated block.
It produces memory fragmentation: it may not allow the allocation of a block with a size equal to the free memory size.
Unlike the Graphics Engine’s allocator, the C module’s allocator adds some utility functions to get information about the heap:
total size,
free size,
number of allocated blocks.
A third-party allocator can replace this allocator and the one in the Graphics Engine.
Files
Implements the functions of
LLUI_DISPLAY_impl.hwithLLUI_DISPLAY_IMPL_imageHeapprefix.C file:
LLUI_DISPLAY_HEAP_impl.c.Status: optional.
Usage
To use the Graphics Engine’s allocator, do not add the file
LLUI_DISPLAY_HEAP_impl.cin the BSP project.To use the C module’s allocator, add the file
LLUI_DISPLAY_HEAP_impl.cin the BSP project.To use a third-party allocator, do not add the file
LLUI_DISPLAY_HEAP_impl.cin the BSP project and implement theLLUI_DISPLAY_IMPL_imageHeapXXXfunctions.
Events Logger
Overview
This part is only mandatory when the BSP calls LLUI_INPUT_dump() (see Event Buffer).
If not included, the call to LLUI_INPUT_dump() performs nothing.
It aims to log the MicroUI events and provide an events dumper.
The logger adds some metadata to each MicroUI event in a dedicated array.
When the BSP is calling LLUI_INPUT_dump(), the logger is using its data to decode the events.
Then, it uses an implementation of microui_event_decoder.h to describe the events.
Files
Implements the functions of
LLUI_INPUT_impl.hwithLLUI_INPUT_IMPL_log_prefix.C files:
LLUI_INPUT_LOG_impl.candmicroui_event_decoder.c.Status: optional.
Usage (to enable the events logger)
Add all C files in the BSP project.
Configure the options in
ui_configuration.h(by default, the logger is disabled).
Buffer Refresh Strategy
Overview
This part provides three Buffer Refresh Strategies (BRS): predraw, single and legacy.
Refer to the chapter Buffer Refresh Strategy for more information about these strategies.
These strategies are optional.
When no strategy is selected, the BSP should provide its own strategy.
If no strategy is specified or provided, a default strategy will be used; this is a minimal, naive strategy, which should only be used when using the Direct Buffer mode.
Some strategies require an implementation of UI_DISPLAY_BRS_restore() (see ui_display_brs.h).
A weak implementation is available; this implementation uses the function memcpy().
Files
Implements the functions of
LLUI_DISPLAY_impl.hrelated to the Buffer Refresh Strategy:LLUI_DISPLAY_IMPL_refresh()andLLUI_DISPLAY_IMPL_newDrawingRegion().C files:
ui_display_brs_legacy.c,ui_display_brs_predraw.c,ui_display_brs_single.c,ui_display_brs.candui_rect_util.c.Status: optional.
Usage
Add all C files in the BSP project (whatever the strategy).
Configure the options in
ui_configuration.h.Comment the line
#error [...]".(optional) Implement
UI_DISPLAY_BRS_restore()(using a GPU, for instance).
C Module: MicroUI Over DMA2D
Overview
This C module is a specific implementation of the C module MicroUI over STM32 DMA2D (Chrom-ART Graphics Accelerator):
It implements a set of drawings using the official Chrom-ART Graphics Accelerator API.
It is compatible with several STM32 MCU:
STM32F4XX,STM32F7XXandSTM32H7XX.It manages several configurations of memory cache.
It is compatible with the multiple destination formats module (but can only handle one destination format).
It is compatible with the Buffer Refresh Strategies (BRS)
predraw,singleandlegacy(switch).
This C module is available on the Developer Repository: com.microej.clibrary.llimpl#microui-dma2d.
Files
Implements some functions of
ui_drawing.h(see above).C file:
ui_drawing_dma2d.c.Status: optional.
Usage
Install the C Module for MicroUI and follow its implementation rules.
Add the C file to the BSP project.
Add the BSP global define
DRAWING_DMA2D_BPPto specify the destination format: 16, 24, or 32 respectivelyDMA2D_RGB565,DMA2D_RGB888andDMA2D_ARGB8888.Call
UI_DRAWING_DMA2D_initialize()fromLLUI_DISPLAY_IMPL_initialize().Check the port by running the
uivalidation as described in the VEE Port project template
Drawings
The following table describes the accelerated drawings:
Feature |
Comment |
|---|---|
Fill rectangle |
|
Draw image |
ARGB8888, RGB888, RGB565, ARGB1555, ARGB4444, A8, A4 [1] |
Cache
Some STM32 MCUs use a memory cache.
This cache must be cleared before using the DMA2D:
Before the call to
HAL_DMA2D_Start_IT().Before the call to
HAL_DMA2D_BlendingStart_IT().
Usage
Check the configuration of the define
DRAWING_DMA2D_CACHE_MANAGEMENTinui_dma2d_configuration.h.
Buffer Refresh Strategy “Predraw”
This strategy requires the copying of some regions from the front buffer to the back buffer on demand (function UI_DISPLAY_BRS_restore(), see above).
To perform these copies, this CCO uses the UI_DRAWING_DMA2D_xxx_memcpy() functions.
Usage
The function
UI_DRAWING_DMA2D_IRQHandler()must be called from the DMA2D IRQ routine.The function
UI_DRAWING_DMA2D_memcpy_callback()should not be implemented (useless).
Example of Implementation
void LLUI_DISPLAY_IMPL_flush(MICROUI_GraphicsContext* gc, uint8_t flush_identifier, const ui_rect_t regions[], size_t length) {
// store the flush identifier
g_current_flush_identifier = flush_identifier;
// change the front buffer address
HAL_LTDC_SetAddress(&hLtdcHandler, (uint32_t)LLUI_DISPLAY_getBufferAddress(&gc->image), LTDC_ACTIVE_LAYER);
// ask an interrupt for the next LCD tick
lcd_enable_interrupt();
}
void LTDC_IRQHandler(LTDC_HandleTypeDef *hltdc) {
// LTDC register reload
__HAL_LTDC_ENABLE_IT(hltdc, LTDC_IT_RR);
// notify the MicroUI Graphics Engine
uint8_t* buffer = (uint8_t*)(BACK_BUFFER == LTDC_Layer->CFBAR ? FRAME_BUFFER : BACK_BUFFER);
LLUI_DISPLAY_setBackBuffer(g_current_flush_identifier, buffer, from_isr);
}
void DMA2D_IRQHandler(void) {
// call CCO DMA2D function
UI_DRAWING_DMA2D_IRQHandler();
}
Buffer Refresh Strategy “Single”
Usually, this strategy is used when the front buffer cannot be mapped dynamically: the same buffer is always used as the back buffer.
However, the front buffer can be mapped on a memory buffer that is in the CPU address range.
In that case, the UI_DRAWING_DMA2D_xxx_memcpy() functions can be used to copy the content of the back buffer to the front buffer.
Usage
The function
UI_DRAWING_DMA2D_configure_memcpy()must be called from the implementation ofLLUI_DISPLAY_IMPL_flush().The function
UI_DRAWING_DMA2D_start_memcpy()must be called from the LCD controller IRQ routine.The function
UI_DRAWING_DMA2D_IRQHandler()must be called from the DMA2D IRQ routine.The function
UI_DRAWING_DMA2D_memcpy_callback()must be implemented to unlock the MicroUI Graphics Engine.
Example of Implementation
void LLUI_DISPLAY_IMPL_flush(MICROUI_GraphicsContext* gc, uint8_t flush_identifier, const ui_rect_t regions[], size_t length) {
// store the flush identifier
g_current_flush_identifier = flush_identifier;
// configure the copy to launch at the next LCD tick
UI_DRAWING_DMA2D_configure_memcpy(LLUI_DISPLAY_getBufferAddress(&gc->image), (uint8_t*)LTDC_Layer->CFBAR, regions[0].x1, regions[0].y1, regions[0].x2, regions[0].y2, RK043FN48H_WIDTH, &dma2d_memcpy);
// ask an interrupt for the next LCD tick
lcd_enable_interrupt();
}
void LTDC_IRQHandler(LTDC_HandleTypeDef *hltdc) {
// clear interrupt flag
LTDC->ICR = LTDC_IER_FLAG;
// launch the copy from the back buffer to the front buffer
UI_DRAWING_DMA2D_start_memcpy(&dma2d_memcpy);
}
void DMA2D_IRQHandler(void) {
// call CCO DMA2D function
UI_DRAWING_DMA2D_IRQHandler();
}
void UI_DRAWING_DMA2D_memcpy_callback(bool from_isr) {
// notify the MicroUI Graphics Engine
LLUI_DISPLAY_setBackBuffer(g_current_flush_identifier, (uint8_t*)BACK_BUFFER, from_isr);
}
Buffer Refresh Strategy “Legacy”
This strategy requires copying the previous drawings from the front buffer to the back buffer before unlocking the MicroUI Graphics Engine.
To perform this copy, this CCO uses the UI_DRAWING_DMA2D_xxx_memcpy() functions.
At the end of the copy, the MicroUI Graphics Engine is unlocked: a new drawing can be performed in the new back buffer.
Usage
The function
UI_DRAWING_DMA2D_configure_memcpy()must be called from the implementation ofLLUI_DISPLAY_IMPL_flush().The function
UI_DRAWING_DMA2D_start_memcpy()must be called from the LCD controller IRQ routine.The function
UI_DRAWING_DMA2D_IRQHandler()must be called from the DMA2D IRQ routine.The function
UI_DRAWING_DMA2D_memcpy_callback()must be implemented to unlock the MicroUI Graphics Engine.
Example of Implementation
void LLUI_DISPLAY_IMPL_flush(MICROUI_GraphicsContext* gc, uint8_t flush_identifier, const ui_rect_t regions[], size_t length) {
// store the flush identifier
g_current_flush_identifier = flush_identifier;
// configure the copy to launch at the next LCD tick
UI_DRAWING_DMA2D_configure_memcpy(LLUI_DISPLAY_getBufferAddress(&gc->image), (uint8_t*)LTDC_Layer->CFBAR, regions[0].x1, regions[0].y1, regions[0].x2, regions[0].y2, RK043FN48H_WIDTH, &dma2d_memcpy);
// change the front buffer address
HAL_LTDC_SetAddress(&hLtdcHandler, (uint32_t)LLUI_DISPLAY_getBufferAddress(&gc->image), LTDC_ACTIVE_LAYER);
// ask an interrupt for the next LCD tick
lcd_enable_interrupt();
}
void HAL_LTDC_ReloadEventCallback(LTDC_HandleTypeDef *hltdc) {
// LTDC register reload
__HAL_LTDC_ENABLE_IT(hltdc, LTDC_IT_RR);
// launch the copy from the new front buffer to the new back buffer
UI_DRAWING_DMA2D_start_memcpy(&dma2d_memcpy);
}
void DMA2D_IRQHandler(void) {
// call CCO DMA2D function
UI_DRAWING_DMA2D_IRQHandler();
}
void UI_DRAWING_DMA2D_memcpy_callback(bool from_isr) {
// notify the MicroUI Graphics Engine
uint8_t* buffer = (uint8_t*)(BACK_BUFFER == LTDC_Layer->CFBAR ? FRAME_BUFFER : BACK_BUFFER);
LLUI_DISPLAY_setBackBuffer(g_current_flush_identifier, buffer, from_isr);
}
C Module: MicroUI Over VGLite
Overview
This C module is a specific implementation of the C module MicroUI over the VGLite library 3.0.15_rev7:
It implements a set of drawings over the official VGLite library 3.0.15_rev7.
It is compatible with the multiple destination formats module.
This C module also provides a set of header files (and their implementations) to manipulate some MicroUI concepts over the VGLite library: image management, path format, etc.: ui_vglite.h and ui_drawing_vglite_path.h.
This C module is available on the Developer Repository: com.microej.clibrary.llimpl#microui-vglite.
Files
Implements some functions of
ui_drawing.h(see above).C files:
mej_math.c,ui_drawing_vglite_path.c,ui_drawing_vglite_process.c,ui_drawing_vglite.candui_vglite.c.Status: optional.
Usage
Install the C Module for MicroUI and follow its implementation rules.
Add the C files to the BSP project.
Call
UI_VGLITE_initializefromLLUI_DISPLAY_IMPL_initializebefore calling any VGLite-related function.Call
UI_VGLITE_startfromLLUI_DISPLAY_IMPL_initializeafter configuring the VGLite library.Configure the options in
ui_vglite_configuration.h.Comment the line
#error [...]".Call
UI_VGLITE_IRQHandlerduring the GPU interrupt routine.Set the VGLite library’s preprocessor define
VG_DRIVER_SINGLE_THREAD.The VGLite library must be patched to be compatible with this C module:
cd [...]/sdk/middleware/vglite patch -p1 < [...]/3.0.15_rev7.patch
In the file
vglite_window.c, add the functionVGLITE_CancelSwapBuffers()and its prototype invglite_window.h:
void VGLITE_CancelSwapBuffers(void) { fb_idx = fb_idx == 0 ? (APP_BUFFER_COUNT - 1) : (fb_idx ) - 1; }
Check the port by running the
uivalidation as described in the VEE Port project template
Options
This C module provides some drawing algorithms that are disabled by default.
The rendering time of a simple shape with the GPU (time in the VGLite library + GPU setup time + rendering time) is longer than with software rendering. To enable the hardware rendering for simple shapes, uncomment the definition of
VGLITE_USE_GPU_FOR_SIMPLE_DRAWINGSinui_vglite_configuration.h.The rendering time of an RGB565 image into an RGB565 buffer without applying an opacity (alpha == 0xff) is longer than with software rendering (as this kind of drawing consists in performing a memory copy). To enable the hardware rendering for RGB565 images, uncomment the definition of
VGLITE_USE_GPU_FOR_RGB565_IMAGESinui_vglite_configuration.h.ARGB8888, ARGB1555, and ARGB4444 transparent images may not be compatible with some revisions of the VGLite GPU. Older GPU revisions do not render transparent images correctly because the pre-multiplication of the pixel opacity is not propagated to the pixel color components. To force the hardware rendering for non-premultiplied transparent images when the VGLite GPU is not compatible, uncomment the definition of
VGLITE_USE_GPU_FOR_TRANSPARENT_IMAGESinui_vglite_configuration.h. Note that this limitation does not concern the VGLite GPU, which is compatible with non-premultiplied transparent images and the A8/A4 formats.
Drawings
The following table describes the accelerated drawings:
Feature |
Comment |
|---|---|
Draw line |
Disabled by default (see above) |
Fill rectangle |
Disabled by default (see above) |
Draw rounded rectangle |
Disabled by default (see above) |
Fill rounded rectangle |
|
Draw circle arc |
Disabled by default (see above) |
Fill circle arc |
|
Draw ellipse arc |
Disabled by default (see above) |
Fill ellipse arc |
|
Draw ellipse arc |
Disabled by default (see above) |
Fill ellipse arc |
|
Draw circle |
Disabled by default (see above) |
Fill circle |
|
Draw image |
ARGB8888_PRE, ARGB1555_PRE, ARGB4444_PRE, RGB565, A8, A4 ARGB8888, ARGB1555, ARGB4444 (see above) |
Draw thick faded point |
Only with fade <= 1 |
Draw thick faded line |
Only with fade <= 1 |
Draw thick faded circle |
Only with fade <= 1 |
Draw thick faded circle arc |
Only with fade <= 1 |
Draw thick faded ellipse |
Only with fade <= 1 |
Draw thick line |
|
Draw thick circle |
|
Draw thick circle arc |
|
Draw thick ellipse |
|
Draw flipped image |
See draw image |
Draw rotated image |
See draw image |
Draw scaled image |
See draw image |
Compatibility With MCU i.MX RT595
UI Pack 13
The versions of the C Module Over VGLite (before 7.0.0) included an implementation of the Low-Level API LLUI_DISPLAY_impl.h.
This support has been extracted into a dedicated C Module since the version 7.0.0.
The dedicated C Module is available on the Developer Repository: com.microej.clibrary.llimpl#microui-mimxrt595-evk.
Only the C Module com.microej.clibrary.llimpl#microui-vglite is useful to target the Vivante VGLite GPU to perform the MicroUI and MicroVG drawings. The C Module com.microej.clibrary.llimpl#microui-mimxrt595-evk only gives an example of an implementation compatible with the MCU i.MX RT595 MCU.
Note
For more information, see the migration notes.
UI Pack 14
Since UI Pack 14, this C module is not compatible anymore and is not maintained.
C Module: MicroUI Over NemaGFX
Overview
This C module is a specific implementation of the C module MicroUI over the Think Silicon NemaGFX:
It implements a set of drawings over the official Think Silicon NemaGFX.
It is compatible with the multiple destination formats module (but it can only handle one destination format).
This C module is available on the Developer Repository: com.microej.clibrary.llimpl#microui-nemagfx.
Files
Implements some functions of
ui_drawing.h(see above).C files:
ui_nema.candui_drawing_nema.c.Status: optional.
Usage
Install the C Module for MicroUI and follow its implementation rules.
Add the C files to the BSP project.
Add
ui_nemagfx/incto the include path.Call
UI_NEMA_initialize()fromLLUI_DISPLAY_IMPL_initialize().Configure the options in
ui_nema_configuration.h.Comment the line
#error [...]".Check the port by running the
uivalidation as described in the VEE Port project template
Implementation
The MicroUI Graphics Engine waits for the end of the asynchronous drawings (performed by the GPU).
The VEE Port must stop this wait with a call to the function UI_NEMA_post_operation() in the GPU interrupt routine.
Tip
The GPU interrupt routine is often written in the same file as the implementation of nema_sys_init().
Options
This C module provides some drawing algorithms that are disabled by default.
The rendering time of a simple shape with the GPU (time in the NemaGFX library + GPU setup time + rendering time) is longer than with software rendering. To enable the hardware rendering for simple shapes, uncomment the definition of
ENABLE_SIMPLE_LINESinui_nema_configuration.h.The rendering of thick faded lines with the GPU is disabled by default: the quality of the rendering is too random. To enable it, uncomment the definition of
ENABLE_FADED_LINESinui_nema_configuration.h.Some GPUs might not be able to render the images in specific memories. Comment the define
ENABLE_IMAGE_ROTATIONinui_nema_configuration.hto not use the GPU to render the rotated images.
Drawings
The following table describes the accelerated drawings:
Feature |
Comment |
|---|---|
Draw line |
|
Draw horizontal line |
Disabled by default (see above: ENABLE_SIMPLE_LINES) |
Draw vertical line |
Disabled by default (see above: ENABLE_SIMPLE_LINES) |
Draw rectangle |
Disabled by default (see above: ENABLE_SIMPLE_LINES) |
Fill rectangle |
|
Draw rounded rectangle |
|
Fill rounded rectangle |
|
Draw circle |
|
Fill circle |
|
Draw image |
ARGB8888, RGB565, A8 |
Draw thick faded line |
Only with fade <= 1 |
Draw thick faded circle |
Only with fade <= 1 |
Draw thick line |
Disabled by default (see above: ENABLE_FADED_LINES) |
Draw thick circle |
|
Draw rotated image |
See draw image |
Draw scaled image |
See draw image |
Compatibility
The compatibility between the components (Packs, C modules, and Libraries) is described in the C Modules.
