Shielded Plug (SP)
Principle
The Shielded Plug (SP) library provides data segregation with a clear publish-subscribe API. The data-sharing between modules uses the concept of shared memory blocks, with introspection. The database is made of blocks: chunks of RAM.

A Shielded Plug Between Two Application (Java/C) Modules.
Documentation |
Link |
Java APIs |
https://repository.microej.com/javadoc/microej_5.x/apis/ej/sp/package-summary.html |
Specification |
https://repository.microej.com/packages/ESR/ESR-SPE-0014-SP-2.0-B.pdf |
Module |
Functional Description
The usage of the Shielded Plug (SP) starts with the definition of a database. The implementation uses an XML file description to describe the database; the syntax follows the one proposed by the [SP] specification.
Once this database is defined, it can be accessed within the MicroEJ
Application or the C application. The SP Foundation Library is
accessible from the [SP] API Module. This library contains
the classes and methods to read and write data in the database. The C header file sp.h available in the MicroEJ
Platform source/include folder contains the C functions for
accessing the database.
To embed the database in your binary file, the XML file description
must be processed by the SP compiler. This compiler generates a binary
file (.o) that will be linked to the overall application by the linker.
It also generates two descriptions of the block ID constants, one in
Java code and one in C code. These constants can be used by either the Java code or the
C application modules.
Shielded Plug Compiler
A MicroEJ tool is available to launch the compiler. The tool name is Shielded Plug Compiler. It outputs:
A description of the requested resources of the database as a binary file (
.o) that will be linked to the overall application by the linker. It is an ELF format description that reserves both the necessary RAM and the necessary Flash memory for the Shielded Plug database.Two descriptions, one in Java code and one in C code, of the block ID constants to be used by either Java or C application modules.
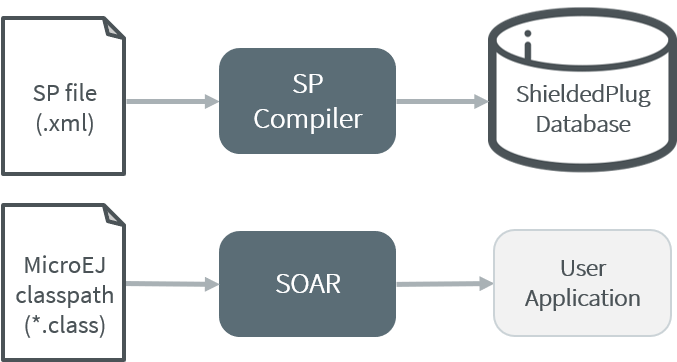
Shielded Plug Compiler Process Overview
Example
Below is an example of using a database. The code that publishes the
data is written in C, and the code that receives the data is written in
Java code. The data is transferred using two memory blocks. TEMP is a scalar
value, THERMOSTAT is a boolean.
Database Description
The database is described as follows:
<shieldedPlug>
<database name="Forecast" id="0" immutable="true" version="1.0.0">
<block id="1" name="TEMP" length="4" maxTasks="1"/>
<block id="2" name="THERMOSTAT" length="4" maxTasks="1"/>
</database>
</shieldedPlug>
Java Code
From the database description we can create an interface.
public interface Forecast {
public static final int ID = 0;
public static final int TEMP = 1;
public static final int THERMOSTAT = 2;
}
Below is the task that reads the published temperature and controls the thermostat.
public void run(){
ShieldedPlug database = ShieldedPlug.getDatabase(Forecast.ID);
while (isRunning) {
//reading the temperature every 30 seconds
//and update thermostat status
try {
int temp = database.readInt(Forecast.TEMP);
print(temp);
//update the thermostat status
database.writeInt(Forecast.THERMOSTAT,temp>tempLimit ? 0 : 1);
}
catch(EmptyBlockException e){
print("Temperature not available");
}
sleep(30000);
}
}
C Code
Here is a C header that declares the constants defined in the XML description of the database.
#define Forecast_ID 0
#define Forecast_TEMP 1
#define Forecast_THERMOSTAT 2
Below, the code shows the publication of the temperature and thermostat controller task.
void temperaturePublication() {
ShieldedPlug database = SP_getDatabase(Forecast_ID);
int32_t temp = temperature();
SP_write(database, Forecast_TEMP, &temp);
}
void thermostatTask(){
int32_t thermostatOrder;
ShieldedPlug database = SP_getDatabase(Forecast_ID);
while(1){
SP_waitFor(database, Forecast_THERMOSTAT);
SP_read(database, Forecast_THERMOSTAT, &thermostatOrder);
if(thermostatOrder == 0) {
thermostatOFF();
}
else {
thermostatON();
}
}
}
Dependencies
LLSP_impl.himplementation (see LLSP: Shielded Plug).
Installation
The [SP] library and its relative tools are an optional feature of the VEE Port.
The installation process is different in SDK 5 and SDK 6:
In the VEE Port configuration file, add the following property:
com.microej.runtime.shieldedplug.enabled=true
In the VEE Port configuration file, check Java to C Interface > Shielded Plug to install the library and its relative tools.
Use
The Shielded Plug API Module must be added to the project build file:
implementation("ej.api:sp:2.0.4")
<dependency org="ej.api" name="sp" rev="2.0.4"/>
This library provides a set of options. Refer to the chapter Standalone Application Options which lists all available options.
