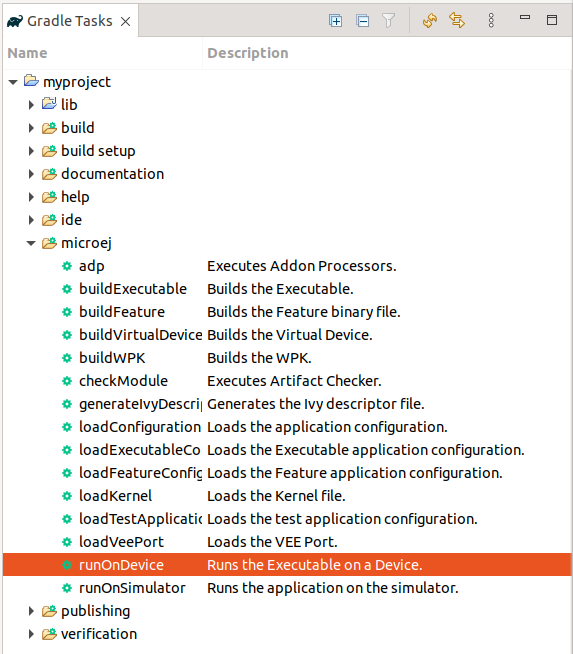
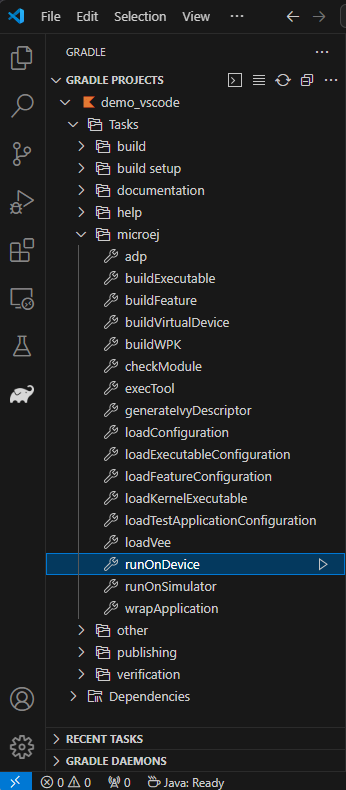
Run on Device
The SDK allows to deploy an Application on a Device thanks to the Gradle runOnDevice task.
The prerequisites of this task are:
The Application EntryPoint must be configured, as described in Configure a Project.
The target VEE Port must be defined. Refer to the Select a VEE Port page to know the different ways to provide a VEE Port for a module project.
The Device must be connected to the developer’s computer.
The configuration required by the VEE Port must be set. Refer to the VEE Port documentation to check the required configuration.
Once these prerequisites are fulfilled, the Application can be deployed on the Device:
By double-clicking on the runOnDevice task in the Gradle tasks view:
Warning
Android Studio does not allow to run multiple Gradle tasks in parallel. If you still want to execute several Gradle tasks simultaneously, you can launch them from a terminal with the Gradle Command Line Interface (CLI).
From the command line interface:
$ ./gradlew runOnDevice
The build should be successful and the output should end with:
Execution of script '<RUN_SCRIPT_PATH>' done.
BUILD SUCCESSFUL
where RUN_SCRIPT_PATH is the absolute path to the run.[sh|bat] script of the VEE Port.
The Application Executable is now deployed on the Device.
Deploying the Executable without building it
When executing the runOnDevice task, the Executable is always rebuilt,
even if nothing has changed in the project.
This ensures that the Executable is always up-to-date, no matter if the BSP has changed or not.
If you want to deploy the Executable on the device without building it (so simply
deploying the Executable file already available in the project build folder),
you can exclude the buildExecutable task:
$ ./gradlew runOnDevice -x buildExecutable
You can execute such a command in IDEs by creating custom configurations, as explained in How To Create a Custom Configuration in the IDE.