Troubleshooting
Java Compiler Version Issue
The SDK requires a JDK 11, so when a JDK 8 is used, the following kind of errors are raised:
When fetching the MicroEJ Gradle plugin:
A problem occurred configuring root project 'myProject'. > Could not resolve all files for configuration ':classpath'. > Could not resolve com.microej.gradle.plugins:plugins:0.3.0. Required by: project : > com.microej.gradle.addon-library:com.microej.gradle.addon-library.gradle.plugin:0.3.0:20221118.151454-1 > No matching variant of com.microej.gradle.plugins:plugins:0.3.0:20221118.151454-1 was found. The consumer was configured to find a runtime of a library compatible with Java 8, packaged as a jar, and its dependencies declared externally, as well as attribute 'org.gradle.plugin.api-version' with value '7.4' but: - Variant 'apiElements' capability com.microej.gradle.plugins:plugins:0.3.0 declares a library, packaged as a jar, and its dependencies declared externally: - Incompatible because this component declares an API of a component compatible with Java 11 and the consumer needed a runtime of a component compatible with Java 8 - Other compatible attribute: - Doesn't say anything about org.gradle.plugin.api-version (required '7.4') - Variant 'javadocElements' capability com.microej.gradle.plugins:plugins:0.3.0 declares a runtime of a component, and its dependencies declared externally: - Incompatible because this component declares documentation and the consumer needed a library - Other compatible attributes: - Doesn't say anything about its target Java version (required compatibility with Java 8) - Doesn't say anything about its elements (required them packaged as a jar) - Doesn't say anything about org.gradle.plugin.api-version (required '7.4') - Variant 'runtimeElements' capability com.microej.gradle.plugins:plugins:0.3.0 declares a runtime of a library, packaged as a jar, and its dependencies declared externally: - Incompatible because this component declares a component compatible with Java 11 and the consumer needed a component compatible with Java 8 - Other compatible attribute: - Doesn't say anything about org.gradle.plugin.api-version (required '7.4') - Variant 'sourcesElements' capability com.microej.gradle.plugins:plugins:0.3.0 declares a runtime of a component, and its dependencies declared externally: - Incompatible because this component declares documentation and the consumer needed a library - Other compatible attributes: - Doesn't say anything about its target Java version (required compatibility with Java 8) - Doesn't say anything about its elements (required them packaged as a jar) - Doesn't say anything about org.gradle.plugin.api-version (required '7.4')
When using the MicroEJ Gradle plugin:
Cause: com/microej/gradle/plugins/MicroejApplicationGradlePlugin has been compiled by a more recent version of the Java Runtime (class file version 55.0), this version of the Java Runtime only recognizes class file versions up to 52.0
The solution is to use a JDK 11 or a higher LTS version (11, 17 or 21) to fix this error:
For the command line interface, make sure that a supported JDK version is defined in the
PATHenvironment. To check, runjava -version. You should see something like this:$ java -version openjdk version "11.0.14.1" 2022-02-08 OpenJDK Runtime Environment Temurin-11.0.14.1+1 (build 11.0.14.1+1) OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM Temurin-11.0.14.1+1 (build 11.0.14.1+1, mixed mode)
Alternatively, you can set the
JAVA_HOMEenvironment variable to point to the installation directory of the JDK.For IntelliJ IDEA and Android Studio, go to File > Settings… > Build, Execution, Deployment > Build Tools > Gradle, and make sure the selected Gradle JVM is a supported JDK version:
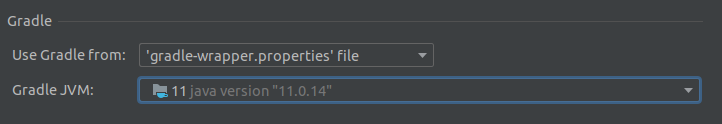
Project JDK in IntelliJ IDEA and Android Studio
Unresolved Dependency When No Repository
If this kind of message appears when resolving plugins or modules dependencies:
* What went wrong:
Plugin [id: 'com.microej.gradle.application', version: '1.4.0'] was not found in any of the following sources:
- Gradle Core Plugins (plugin is not in 'org.gradle' namespace)
- Included Builds (No included builds contain this plugin)
- Plugin Repositories (could not resolve plugin artifact 'com.microej.gradle.application:com.microej.gradle.application.gradle.plugin:1.1.0')
Searched in the following repositories:
Gradle Central Plugin Repository
or this kind:
* What went wrong:
Execution failed for task ':compileJava'.
> Could not resolve all files for configuration ':compileClasspath'.
> Cannot resolve external dependency ej.api:edc:1.3.7 because no repositories are defined.
Required by:
root project :
It means that no module or plugin repository has been defined.
Make sure that the repositories have been configured as described in the Configure Repositories section.
In particular, make sure that the Gradle Init script is in the .gradle/init.d folder in the Gradle User Home folder.
The Gradle User Home folder is defined by default to the OS User Home folder,
and can be changed by setting the GRADLE_USER_HOME environment variable
or in the IDE settings (see Intellij IDEA documentation).
Unresolved Dependency in Repositories
If this kind of message appears when resolving plugins or modules dependencies:
* What went wrong:
Plugin [id: 'com.microej.gradle.application', version: '1.4.0'] was not found in any of the following sources:
- Gradle Core Plugins (plugin is not in 'org.gradle' namespace)
- Included Builds (No included builds contain this plugin)
- Plugin Repositories (could not resolve plugin artifact 'com.microej.gradle.application:com.microej.gradle.application.gradle.plugin:1.4.0')
Searched in the following repositories:
microEJCentral(https://repository.microej.com/modules)
microEJForgeCentral(https://forge.microej.com/artifactory/microej-central-repository-release)
microEJForgeDeveloper(https://forge.microej.com/artifactory/microej-developer-repository-release)
or this kind:
* What went wrong:
Execution failed for task ':compileJava'.
> Could not resolve all files for configuration ':compileClasspath'.
> Could not find com.mycompany:mymodule:M.m.p.
Searched in the following locations:
- https://my-company-first-repository/com/mycompany/mymodule/M.m.p/kf-M.m.p.pom
- https://my-company-first-repository/com/mycompany/mymodule/M.m.p/ivy-M.m.p.xml
- https://my-company-second-repository/com/mycompany/mymodule/M.m.p/kf-M.m.p.pom
- https://my-company-second-repository/com/mycompany/mymodule/M.m.p/ivy-M.m.p.xml
Required by:
project :
First, check that either the requested plugin or module exists in the listed repositories.
If the plugin or module does not exist,
if it is declared as a direct dependency, the module repository is not compatible with your source code. You can either check if another module version is available in the repository or add the missing module to the repository.
otherwise, this is likely a missing transitive module dependency. The module repository is not consistent. Check the module repository and make sure all the transitive dependencies exist.
If the module exists, this may be due to a missing repository in the configuration. Check that your repository appears in the list of URLs below the error line:
Searched in the following locations:If the URL of your repository is not listed, add it to the list of the repositories.
If the repository is correctly configured, this may be a network connection error. We can check in the debug logs, by adding the
--debugarguments in the Gradle command line.
Otherwise, if your module repository is an URL, check for an Invalid SSL Certificate issue.
Invalid SSL Certificate
If a dependency cannot be retrieved from a remote repository, this may be due to a missing or incorrect SSL certificate.
It can be checked in the debug logs, by adding the --debug argument in the Gradle command line, for example:
./gradlew build --debug
If the logs show the SSL handshake start followed immediately by the Connection Shutdown:
2026-01-27T18:01:16.708+0100 [DEBUG] [org.apache.http.conn.ssl.SSLConnectionSocketFactory] Starting handshake 2026-01-27T18:01:16.749+0100 [DEBUG] [org.apache.http.impl.conn.DefaultManagedHttpClientConnection] http-outgoing-69: Shutdown connection 2026-01-27T18:01:16.749+0100 [DEBUG] [org.apache.http.impl.execchain.MainClientExec] Connection discarded
it most likely means that the SSL certificate is missing or incorrect.
This can be raised in several cases, such as:
an artifact repository configured in the MicroEJ Module Manager settings using a self-signed SSL certificate or a SSL certificate not trusted by the JDK.
the requests to an artifact repository configured in the MicroEJ Module Manager settings are redirected to a proxy server using a SSL certificate not trusted by the JDK.
In all cases, the SSL certificate (used by the artifact repository server or the proxy) must be added to the JDK trust store that is running Gradle.
Before updating the SSL certificate, it is recommended to exit all your IDE projects and stop Gradle daemons (all versions).
One simple way is to list all Java processes and kill the ones named GradleDaemon:
./jps
12768
17792 GradleDaemon
16920
4712 Jps
1820 GradleDaemon
Also, if you don’t know which JDK is running Gradle, you can first fix the JDK used by Gradle by following How To Define a Specific Java Home for Gradle.
Ask your System Administrator, or retrieve the SSL certificate and add it to the JDK trust store:
on Windows
Install Keystore Explorer.
Start Keystore Explorer, and open file
[JRE_HOME]/lib/security/cacertsor[JDK_HOME]/jre/lib/security/cacertswith the passwordchangeit. You may not have the right to modify this file. Edit rights if needed before opening it or open Keystore Explorer with admin rights.Click on Tools, then Import Trusted Certificate.
Select your certificate.
Save the
cacertsfile.
on Linux/macOS
Open a terminal.
Make sure the JDK’s
binfolder is in thePATHenvironment variable.Execute the following command:
keytool -importcert -v -noprompt -trustcacerts -alias myAlias -file /path/to/the/certificate.pem -keystore /path/to/the/truststore -storepass changeit
If the problem still occurs, there should be a trace which indicates the beggining of the handshake phase of the SSL negotiation:
2023-12-15T17:32:47.442+0100 [DEBUG] [org.apache.http.conn.ssl.SSLConnectionSocketFactory] Starting handshake
The error very probably occurs during this phase. There should be the following trace before the error:
Consuming server Certificate handshake message
The traces below this one indicates the SSL certificate (or the SSL certificates chain) presented by the server. This certificate or one of the root or intermediate certificates must be added in the JDK truststore as explained previously.
Failing Resolution in adp Task
During the build of a project, the error Cannot locate module version for non-maven layout may be raised:
Execution failed for task ':adp'.
> Could not resolve all files for configuration ':addonProcessorClasspath'.
> Could not download binary-nls-processor-2.4.2.adp (com.microej.tool.addon.runtime:binary-nls-processor:2.4.2)
> Cannot locate module version for non-maven layout.
> Could not download js-processor-0.13.0.adp (com.microej.tool.addon.runtime:js-processor:0.13.0)
> Cannot locate module version for non-maven layout.
> Could not download junit-processor-1.7.1.adp (ej.tool.addon.test:junit-processor:1.7.1)
> Cannot locate module version for non-maven layout.
This is due to a wrong pattern in the declaration of the Ivy repositories.
Check your Ivy repositories and make sure the value of the artifact of the patternLayout block is set to [organisation]/[module]/[revision]/[artifact]-[revision](-[classifier])(.[ext]).
For example:
ivy {
url = uri("https://repository.microej.com/5/artifacts/")
patternLayout {
artifact("[organisation]/[module]/[revision]/[artifact]-[revision](-[classifier])(.[ext])")
ivy("[organisation]/[module]/[revision]/ivy-[revision].xml")
setM2compatible(true)
}
}
Missing Version for Publication
If the following message is displayed when publishing a module:
The project version must be defined.
It means the version property is missing and should be defined in the module build file.
See Publish a Project for more information.
Fail to load a VEE Port as dependency
When a VEE Port is defined as a dependency, the build of the project can fail with the following message:
> No 'release.properties' and 'architecture.properties' files found.
The given file <path/to/file> is not a VEE Port archive.
If the dependency is a valid VEE Port, this error probably means that several artifacts of the VEE Port have been published
with the default Ivy configuration.
To fix this issue, you can select the right artifact by adding information on the one to fetch in the artifact block, for example:
microejVee("com.mycompany:myveeport:1.0.0") {
artifact {
name = "artifact-name"
type = "zip"
}
}
This will select the artifact with the name artifact-name and with the type zip.
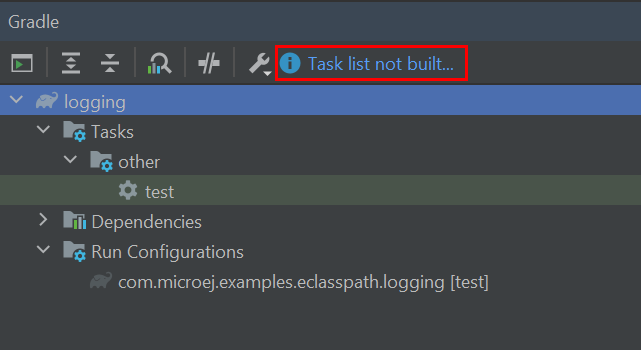
Missing Tasks in the Gradle view of Android Studio
In some cases, Android Studio may not build all the Gradle tasks, the Task list not built… message is displayed:
To build all the Gradle tasks in Android Studio:
Go to File > Settings > Experimental,
Enable the option: Configure all Gradle tasks during Gradle Sync (…).
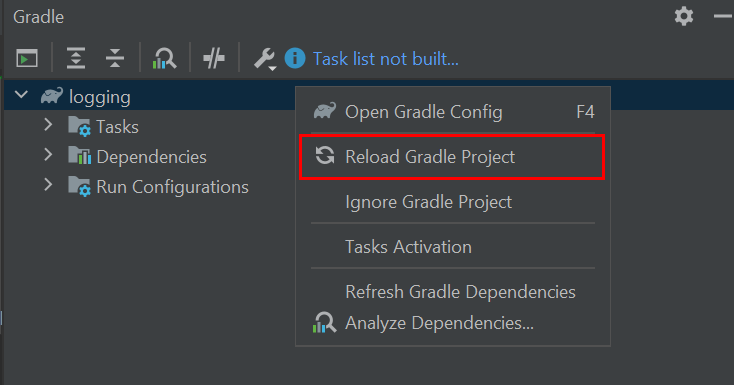
Back in the Gradle task view:
Right-click on the project name,
Select Reload Gradle Project.
Note
By default, all supported IDEs require the user to explicitly trigger the reload of a Gradle project when its configuration has changed. However you can configure your IDE to automatically reload your project. Refer to the How To Automatically reload a Gradle project section for more information.
Code Detected as Unreachable in IntelliJ
When opening MicroEJ project with IntelliJ 2024.1, code is displayed in grey (dead code style) after a call to a MicroEJ Foundation API.
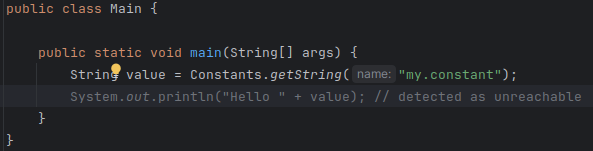
This happens because Foundation API dependencies do not include implementation code but only throw RuntimeException. IntelliJ thus infers
that the code that comes after is unreachable.
The detection of unreachable code can be disabled by going in Settings… > Editor > Inspections and unchecking the option Unreachable code in Java > Probable bugs.
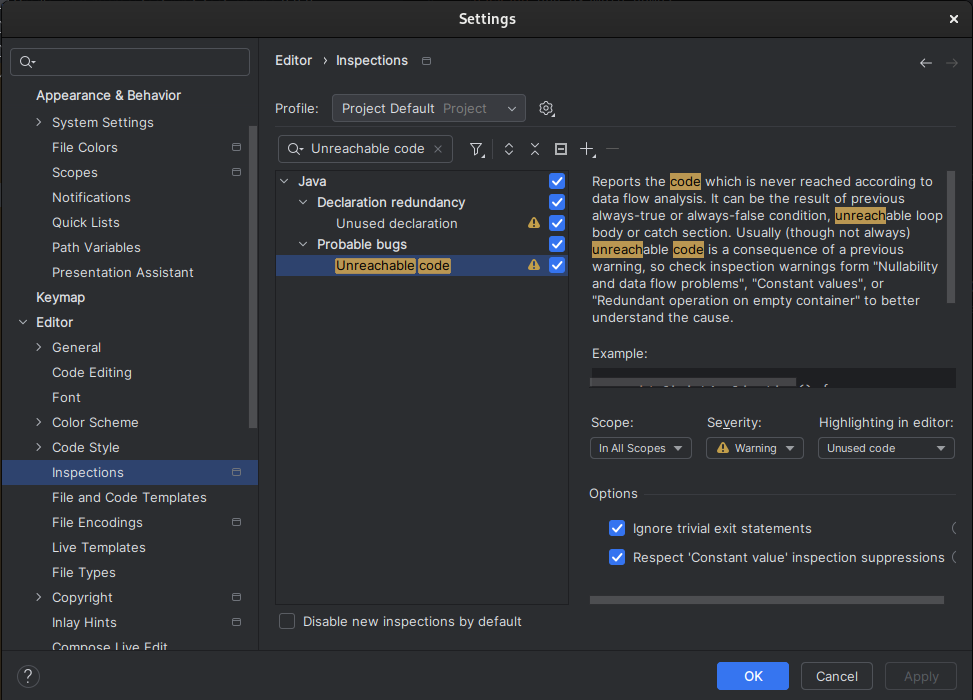
You can also disable unreachable code detection locally by using @SuppressWarnings("UnreachableCode") on the method or on the class.
Resolution Conflict with Testsuite Dependencies
When a project and its testsuite depend on different versions of the same dependency, the build of the project can fail with the following message:
Execution failed for task ':adp'.
> Conflict(s) with a direct dependency for the following module(s):
- ej.api:kf : the resolved version is 1.7.0 whereas the direct dependency version is 1.4.4
To fix this issue, you must update the dependency of your testsuite to use the same version as the project dependency:
dependencies {
implementation("ej.api:edc:1.3.7")
implementation("ej.api:kf:1.7.0")
}
testing {
suites {
val test by getting(JvmTestSuite::class) {
microej.useMicroejTestEngine(this)
dependencies {
implementation(project())
implementation("ej.api:edc:1.3.7")
implementation("ej.api:kf:1.7.0")
implementation("ej.library.test:junit:1.12.0")
implementation("org.junit.platform:junit-platform-launcher:1.8.2")
}
}
}
}
Gradle Build Files (*.kts) Errors in IntelliJ IDEA
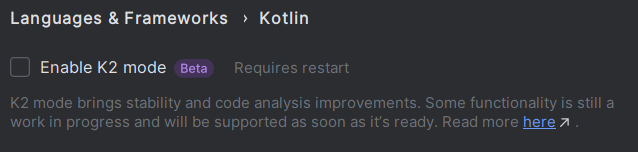
Since version 2025.1, the new Kotlin K2 compiler is enabled by default to compile Gradle build scripts. For now, it requires a JDK in project’s classpath in order to
interpret the build file successfully. MicroEJ projects do not have JDK in classpath, the Gradle build scripts are thus fully marked in red with the following errors:
Cannot access 'Comparable' which is a supertype of 'KotlinBuildScript'. Check your module classpath for missing or conflicting dependencies.
Cannot access 'Object' which is a supertype of 'KotlinBuildScript'. Check your module classpath for missing or conflicting dependencies.
To fix this, you need to
Fail to fetch the prod version of an Architecture
Fetching the prod version of an Architecture may raise the following error:
> Could not find flopi4G25-8.3.0-prod.xpf (com.microej.architecture.CM4.CM4hardfp_GCC48:flopi4G25:8.4.0).
Searched in the following locations:
https://repository.microej.com/modules/com/microej/architecture/CM4/CM4hardfp_GCC48/flopi4G25/8.4.0/flopi4G25-8.4.0-prod.xpf
This happens when a module repository containing only the eval version of the Architecture is declared before the module repository containing the prod version.
This is typically the case with the MicroEJ Central Repository which contains only the eval versions of the public Architecture.
If the prod version is deployed in another repository declared after the MicroEJ Central Repository, the above error is raised.
To fix this, declare the repository containing the prod version before the one containing the eval version.
Refer to How To Add a Repository for more details on how to declare module repositories.
Missing Compilation Capability
During the build of a project (precisely the Java compilation phase), the following error may be raised:
* What went wrong:
Execution failed for task ':compileJava'.
> Error while evaluating property 'javaCompiler' of task ':compileJava'.
> Failed to calculate the value of task ':compileJava' property 'javaCompiler'.
> Toolchain installation 'C:\Program Files (x86)\Eclipse Adoptium\jre-11.0.28.6-hotspot' does not provide the required capabilities: [JAVA_COMPILER]
This means that the Java installation used by Gradle is not a JDK but a JRE, whereas Gradle and the SDK require a JDK. Therefore, the solution is to install and configure a JDK. Refer to Check your JDK version for more information.
Build Errors from JVM Memory Misconfiguration
Below are two examples of error messages that can be raised when the JVM used to launch the VEE scripts is not configured properly. The ouput may vary depending on the Gradle task being executed but the errors share the same root cause.
When building an executable:
=============== [ Launching SOAR ] ===============
1 : ERROR :
[M2] - OutOfMemory error. Try to increase heap space using JVM option '-Xmx' (e.g. '-Xmx4096M')
Terminated with errors
When running on simulator:
=============== [ Launching on Simulator ] ===============
"Internal limits reached. Please contact support@microej.com"
These errors are typically seen when running gradlew buildExecutable or gradlew runOnSimulator if the forked JVM is started with insufficient heap.
To resolve this, adjust the JVM memory configuration by setting the JVM options accordingly with the property microej.launch.jvmargs, for example:
./gradlew buildExecutable -Dmicroej.launch.jvmargs="-Xmx1024m -Xms512m"
No Architecture Defined Error
The following error may be raised when building a project:
Execution failed for task ':loadVee'.
> No Architecture defined. An Architecture can be provided by declaring adependency with the `microejArchitecture` configuration (e.g. `microejArchitecture("com.mycompany:myArchitecture:M.m.p")').
This can happen when a VEE Port built with SDK 6 1.3.0 or higher is provided to a project using an older version of the SDK 6.
To resolve this, update your project to use SDK 6 version 1.2.0 minimum.
Build Errors from JDK / Gradle Incompatibilities in VS Code
Gradle must be run with a compatible JDK version. If the Gradle/JDK compatibility matrix is not respected, project sync or builds may fail, and in VS Code the Java/Gradle integration often reports non-explicit errors, making the root cause difficult to identify.
If you experience the following errors, first verify Gradle/JDK compatibility and either update the Gradle Wrapper or use a supported JDK before further troubleshooting.
JDK 25 with Gradle < 9.1.0
* What went wrong:
25.0.1
JDK 24 and Gradle < 8.14.0
* What went wrong:
Could not create task ':outgoingVariants'.
> Could not create task of type 'OutgoingVariantsReportTask'.
> Could not create an instance of type org.gradle.api.tasks.diagnostics.internal.configurations.ConfigurationReportsImpl.
> Could not create an instance of type org.gradle.api.reporting.internal.DefaultReportContainer.
> Type T not present
JDK 23 and Gradle < 8.10
* What went wrong:
Could not open cp_init generic class cache for initialization script
BUG! exception in phase 'semantic analysis' in source unit '_BuildScript_' Unsupported class file major version 67
> Unsupported class file major version 67
JDK 22 and Gradle < 8.7
* What went wrong:
BUG! exception in phase 'semantic analysis' in source unit '_BuildScript_' Unsupported class file major version 66
> Unsupported class file major version 66
JDK 11 and Gradle 9+
* What went wrong:
[error] [gradle-server] Could not run build action using connection to Gradle distribution 'https://services.gradle.org/distributions/gradle-9.x.x-bin.zip'.
Gradle Build Performance
The following settings can improve Gradle build times.
They can be configured globally in <USER_HOME>/.gradle/gradle.properties, per-project in <PROJECT_ROOT>/gradle.properties, or passed via command line with -D (system property).
JVM Heap Size
Increases memory allocated to the Gradle Daemon, reducing garbage collection overhead for large projects:
org.gradle.jvmargs=-Xmx2048m
File System Watching
Gradle tracks file system changes to optimize incremental builds. This feature can significantly slow down builds in certain environments (e.g., unstable network drives).
Disable it by passing --no-watch-fs in the command line or by setting:
org.gradle.vfs.watch=false
Refer to the Gradle documentation for more configuration options.
Gradle Build Performance: Windows-Specific Optimizations
Gradle builds can be noticeably slower on Windows 10+ due to real-time antivirus scanning, especially Windows Defender. Gradle and the JVM create, read, and delete thousands of small files during dependency resolution, compilation, packaging, and caching. When Windows Defender scans each of these file operations, it adds significant I/O overhead, which directly increases build times, in particular for large projects.
Step 1: Exclude key folders from Windows Defender
To reduce unnecessary scanning and improve Gradle build performance, configure Windows Defender to exclude the following folders (adapt paths to your environment):
C:\Users\<name>\.gradle: Gradle dependency cache, transforms, metadata.C:\Users\<name>\.microej: MicroEJ-specifics (e.g., evaluation licences).C:\path\to\project: project files, or at least all<project>/buildoutput directories.C:\Program Files\Eclipse Adoptium\jdk-11.0.18.10-hotspot: JDK installations used by Gradle/IDEJVM temporary directory (default:
%TEMP%, typicallyC:\Users\<name>\AppData\Local\Temp). Runjava -XshowSettings:properties 2>&1 | findstr java.io.tmpdirto display the current value.C:\Users\<name>\AppData\Local\JetBrains\IntelliJIdea2025.3: IDE caches (example: IntelliJ IDEA)
Note
Some IDEs like IntelliJ IDEA automatically display a notification offering to configure exclusions for project directories and IDE caches. It is recommended to accept this suggestion when prompted.
Windows Defender exclusions can be configured either through the graphical interface or via the command line.
In the Windows Security app, go to Virus & threat protection > Manage settings > Exclusions > Add or remove exclusions, and add the relevant folders as exclusion paths.
Exclusions can also be added from an elevated PowerShell prompt using the following command:
Add-MpPreference -ExclusionPath "C:\path\to\exclude"
You can repeat this command for each directory to exclude, and verify the configuration with:
Get-MpPreference | Select -ExpandProperty ExclusionPath
Step 2: Disable NTFS features that slow down builds (optional)
Windows NTFS enables legacy features that add overhead for file-heavy workloads like Gradle builds.
To prevent NTFS from generating legacy DOS-style filenames for every new file, disable 8.3 filename generation in an elevated PowerShell:
fsutil.exe behavior set disable8dot3 1
To prevent NTFS from updating file “last accessed” timestamps on every read, which reduces extra disk writes:
fsutil.exe behavior set disableLastAccess 3
Warning
These changes may affect other software on the system. Disabling 8.3 filenames can break legacy applications that depend on short DOS-style paths. Disabling last access timestamps may impact backup software using incremental backups based on access time, or file synchronization tools. Refer to the Windows documentation for more details.