Warning
This documentation is for SDK 5. The latest major version is SDK 6. SDK 5 is in maintenance mode since the release of SDK 5.8.0. Consequently, as stated in the SDK End User License Agreement (EULA), the SDK will reach the end of its life by July 2028. Contact our support team for assistance with migrating to the new SDK, or your sales representative if you require an extension of SDK maintenance as a service.
Code Coverage Analyzer
Principle
The Simulator features an option to output .cc (Code Coverage) files that represent the use rate of functions of an application. It traces how the opcodes are really executed.
Functional Description
The Code Coverage Analyzer scans the output .cc files, and outputs an HTML report to ease the analysis of methods coverage. The HTML report is available in a folder named htmlReport in the same folder as the .cc files generated by enabling the Code Coverage option .
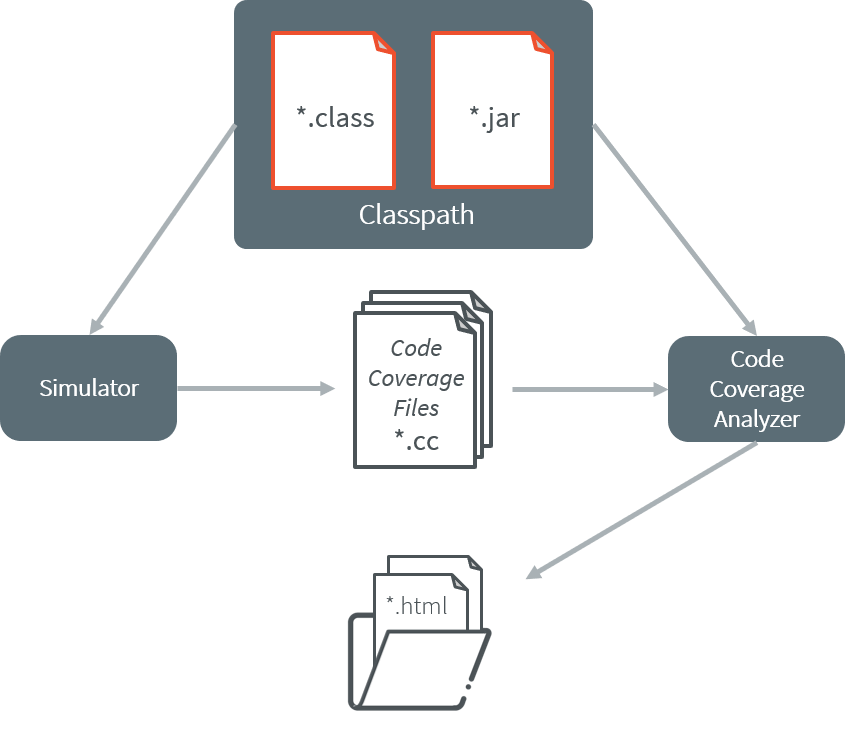
Code Coverage Analyzer Process
Dependencies
In order to work properly, the Code Coverage Analyzer should input the .cc files. The .cc files relay the classpath used during the execution of the Simulator to the Code Coverage Analyzer. Therefore the classpath is considered to be a dependency of the Code Coverage Analyzer.
Installation
This tool is a built-in Architecture tool.
Use
A MicroEJ tool is available to launch the Code Coverage Analyzer tool. The tool name is Code Coverage Analyzer.
Two levels of code analysis are provided, the Java level and the bytecode level. Also provided is a view of the fully or partially covered classes and methods. From the HTML report index, just use hyperlinks to navigate into the report and source / bytecode level code.
Category: Code Coverage
Option(browse): *.cc files folder
Option Name: cc.dir
Default value: (empty)
Description:
Specify a folder which contains the cc files to process (*.cc).
Group: Classes filter
Option(list): Includes
Option Name: cc.includes
Default value: (empty)
Description:
List packages and classes to include to code coverage report. If no package/class is specified, all classes found in the project classpath will be analyzed.
Examples:
packageA.packageB.*: includes all classes which are in package
packageA.packageB
packageA.packageB.className: includes the class
packageA.packageB.className
Option(list): Excludes
Option Name: cc.excludes
Default value: (empty)
Description:
List packages and classes to exclude to code coverage report. If no package/class is specified, all classes found in the project classpath will be analyzed.
Examples:
packageA.packageB.*: excludes all classes which are in package
packageA.packageB
packageA.packageB.className: excludes the class
packageA.packageB.className
