Font
Principle
The Font module contains the C part of the MicroVG implementation, which manages vectorial fonts. This module is composed of two elements:
an implementation of Abstraction Layer APIs to manipulate font files,
an implementation of Abstraction Layer APIs for MicroVG drawings.
Functional Description
The Font module implements the MicroVG VectorFont framework. It provides Abstraction Layer APIs that consist in opening and decoding a font file and getting the font’s characteristics.
A font file:
is either a TTF or an OTF,
is identified by the resource name,
can be stored as internal resource or external (see External Fonts).
No data is stored in the Managed Heap. The implementation is responsible for the font’s cycle life: allocation and release.
A font is used to draw a string with a color or with a linear gradient.
Abstraction Layer API
There are two separate Abstraction Layer API header files (see LLVG_FONT: Vector Font):
LLVG_FONT_impl.hspecifies the Abstraction Layer APIs used to open and retrieve the font’s characteristics.LLVG_PAINTER_impl.hlists the Abstraction Layer APIs called by VectorGraphicsPainter to draw a string with the font.
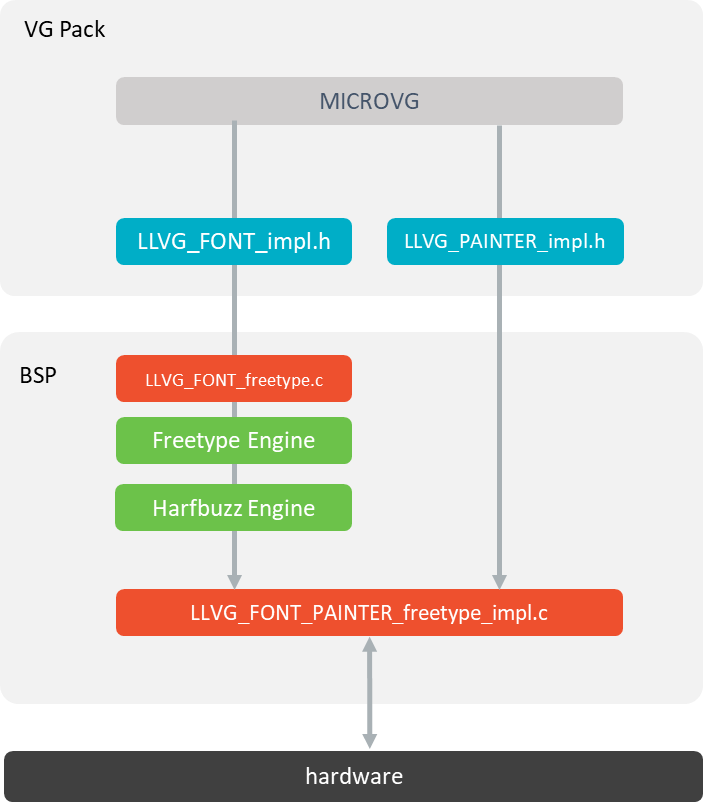
Font Abstraction Layer API
MicroVG library calls the BSP functions through the header files
LLVG_FONT_impl.handLLVG_PAINTER_impl.h.The C module MicroVG provides a default implementation of
LLVG_FONT_impl.hover FreeType. It also redirects the complex layout to a third party C module.This C module also provides an implementation of
LLVG_PAINTER_impl.cthat synchronizes the drawing with the MicroUI Graphics Engine and redirects the drawing itself to a third-party drawer throughvg_drawing.h.A C module dedicated to a GPU provides an implementation of this drawer (
vg_drawing_gpu.c) that implements the drawings over the GPU library.The C module Harfbuzz provides an implementation of complex layout.
These files are automatically copied in the BSP project when fetching the C modules during the VEE Port build.
External Memory
Principle
MicroVG does not provide some Low Level API to make the distinction between a font loaded from different kind of memories (internal or external, byte-addressable or not). The Low Level implementation (C Modules MicroVG and FreeType) features the font management from an external memory which is not byte-addressable when the VEE Port provides an implementation of the External Resources Loader.
Configuration File
A Vector Font file is a simple resource.
To specify this resource as an external resource, the font file path must be listed in a .externresources.list file in addition with the .resources.list file (see Application Resources).
Process
The following steps describe how to setup the loading of an external resource from the application:
Add the font to the application project resources (typically in the source folder
src/main/resourcesand in the packagefonts).Create / open the configuration files (e.g.
application.resources.listandapplication.externresources.list).In both files, add the relative path of the font (e.g.
/fonts/myFont.ttf).Build the application: the processed external resources are copied into the external resources folder (
[application_output_folder]/externalResources).Deploy the external resources to the external memory (SDCard, flash, etc.) of the device.
(optional) Configure the External Resources Loader to load from this source.
Build the application and run it on the device.
The application loads the external resource using ej.microvg.VectorFont.loadFont().
FreeType (C Modules) recognizes this resource as external resource; it configures itself to manage this resource differently than an internal resource (see Library: FreeType to have more details).
The application can use the font.
Simulation
The Simulator automatically manages the external resources like internal resources.
All images listed in *.externresources.list files are copied in the external resources folder, and this folder is added to the Simulator’s classpath.
Use
The MicroVG Font APIs are available in the class ej.microvg. VectorFont.
