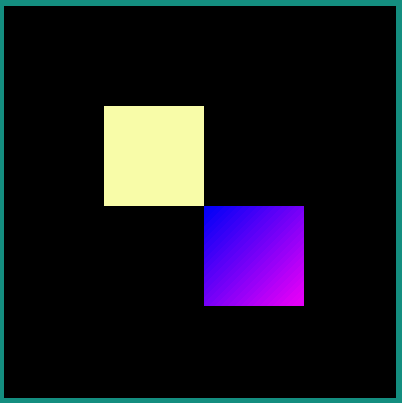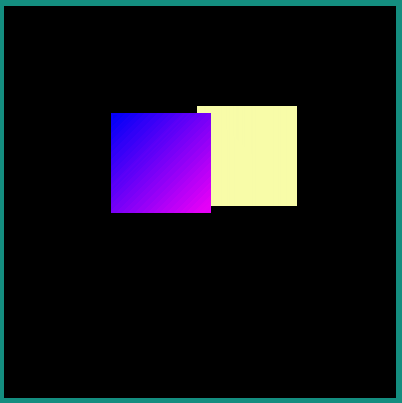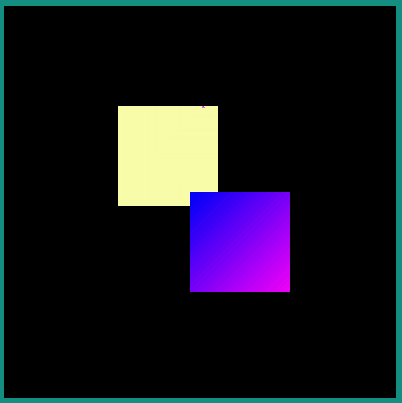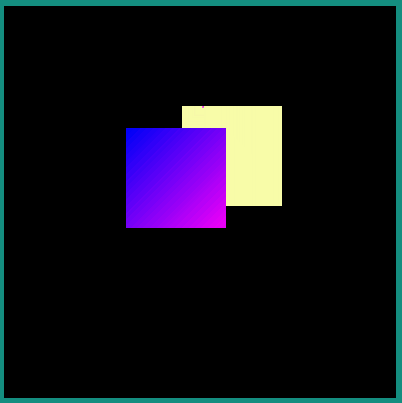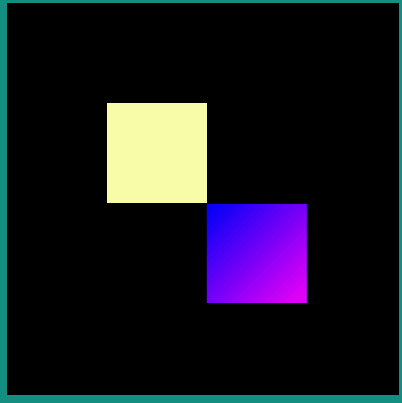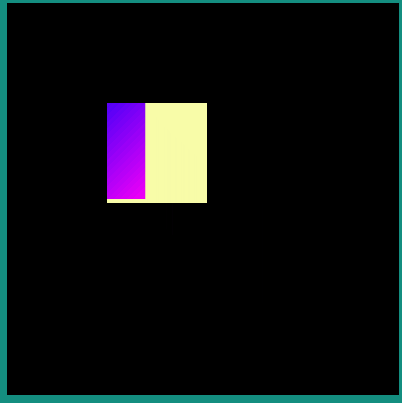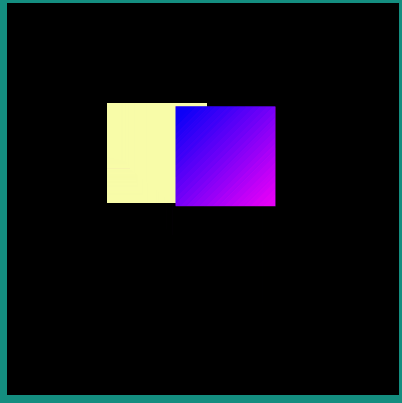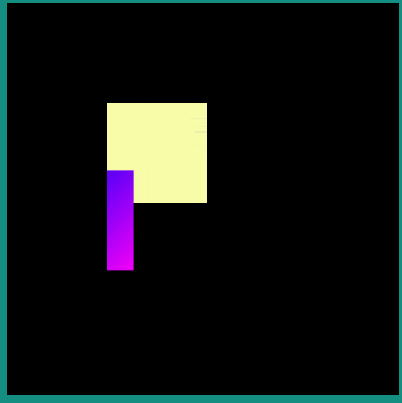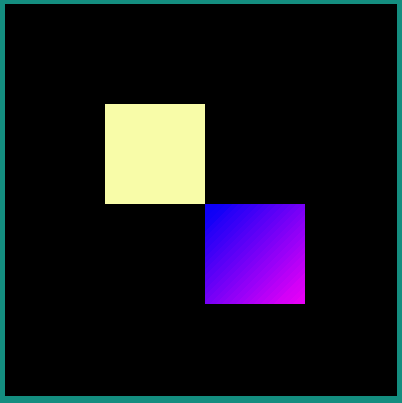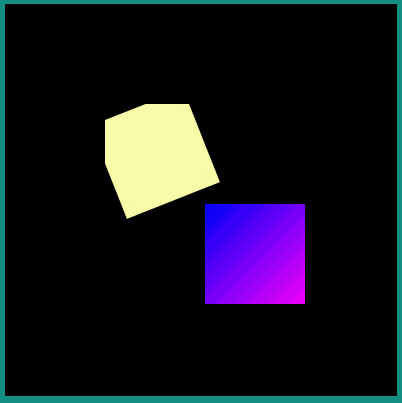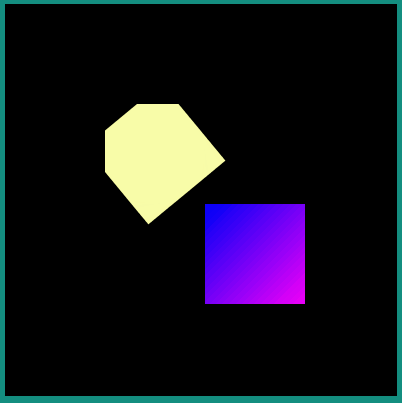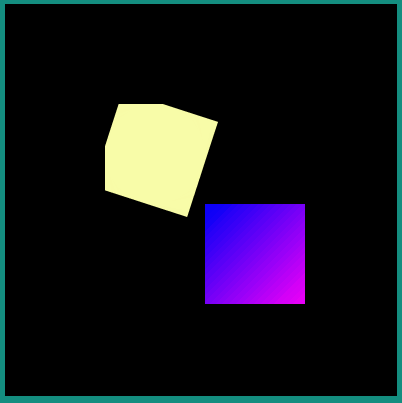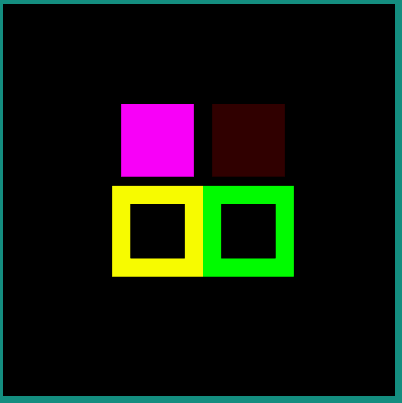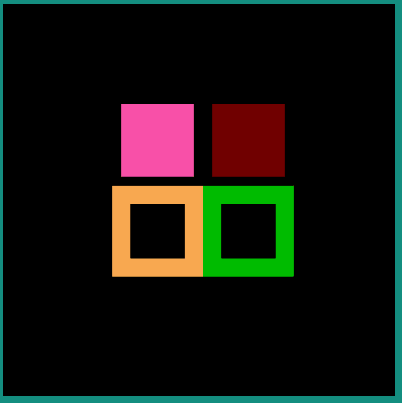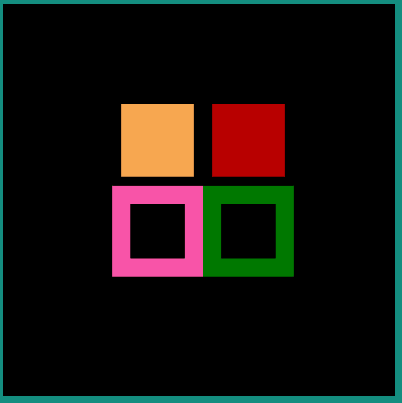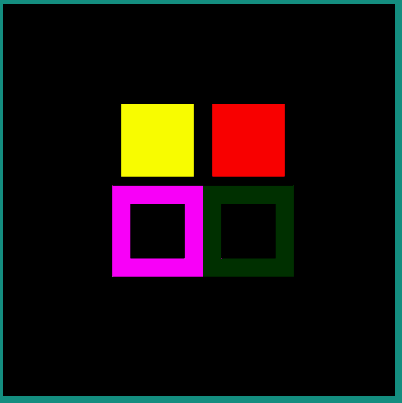Vector Images
Overview
Vector Images are graphical resources that can be accessed with a call to ej.microvg.VectorImage.getImage(). The images are converted at build-time (using the image generator tool) to binary resources.
Images that must be processed by the image generator tool are declared in *.vectorimages.list files (or in *.externvectorimages.list for an external resource, see External Images). The file format is a standard Java properties file, each line representing a / separated resource path relative to the MicroEJ classpath root referring to a vector image file (e.g. .svg, .xml). The resource must be followed by a parameter (separated by a :) which defines and/or describes the image output file format (raw format).
Currently accepted formats are :
:VGF: MicroVG compatible format with coordinates encoded as float numbers (32 bits).:VG32: MicroVG compatible format with coordinates encoded as signed int numbers (32 bits).:VG16: MicroVG compatible format with coordinates encoded as signed short numbers (16 bits).:VG8: MicroVG compatible format with coordinates encoded as signed char numbers (8 bits).
Note
The ouput format may be adjusted by the MicroVG engine to fit the capabilities of the vectorial GPU.
Example:
/com/mycompany/MyImage1.svg:VGF
/com/mycompany/androidVectorDrawable.xml:VG8
Warning
In the case where the output format is not specified, the resource is embedded as is, as described in the Image Generator chapter Unspecified Output Format. This use case is useful for loading an encoded VG image, as described in the Android Vector Drawable Loader chapter.
Supported Input Files
The image generator tool supports the following input file formats:
Android Vector Drawable
SVG
Refer to the Limitations / Supported Features section for the list of supported features for these file formats.
The vector image objects are extracted and converted to paths made of Move, Line and Curve commands.
Each path is associated with either a fill color or a linear gradient. All object strokes are converted to filled paths at build-time.
Objects group transformations are also extracted from the input file and applied at run-time.
Drawing Images
Drawing and Transforming Images
Once an image has been loaded it can be drawn in the graphic context with a call to ej.microvg.VectorGraphicsPainter.drawImage().
The image is associated with a transformation Matrix that will be applied in order to translate, scale and/or rotate the image.
The application can get the width and the height of the image with ej.microvg.VectorImage.getWidth() and ej.microvg.VectorImage.getHeight() to correctly scale and position the image in the application window.
The following example describes how an Android Vector Drawable file can be drawn and positioned on the display.
Android Vector Drawable file:
<vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:aapt="http://schemas.android.com/aapt"
android:width="100dp" android:height="100dp" android:viewportWidth="100" android:viewportHeight="100">
<path android:pathData="M 0 0 h50 v50 h-50 z" android:fillColor="#FFFFAA"/>
<path android:pathData="M 50 50 h50 v50 h-50 z">
<aapt:attr name="android:fillColor">
<gradient
android:startColor="#0000ff" android:startX="50" android:startY="50"
android:endColor="#ff00ff" android:endX="100" android:endY="100"
android:type="linear">
</gradient>
</aapt:attr>
</path>
</vector>
Drawing With Opacity
The vector image can be drawn with a global opacity level.
Warning
As paths are drawn one after the other, images that contain overlapping paths are not correctly colored when a global opacity is applied. The rendering of these images will throw an exception. The images must be reworked to suppress overlapping.
Color Filtering
A VectorImage object can be derived from another VectorImage object, keeping the paths and transformations but updating the colors using a color matrix.
This color matrix is a 4x5 float matrix. It is organized like that:
Each line is used to compute a component of the resulting color, in this order: red, green, blue, alpha.
The four first columns are multipliers applied to a component of the initial color, in this order: red, green, blue, alpha.
The last column is a constant value.
Let A, R, G, B be the components of the initial color and the following array a color matrix:
{ rR, rG, rB, rA, rC, // red
gR, gG, gB, gA, gC, // green
bR, bG, bB, bA, bC, // blue
aR, aG, aB, aA, aC } // alpha
The resulting color components are computed as:
resultRed = rR * R + rG * G + rB * B + rA * A + rC resultGreen = gR * R + gG * G + gB * B + gA * A + gC resultBlue = bR * R + bG * G + bB * B + bA * A + bC resultAlpha = aR * R + aG * G + aB * B + aA * A + aC
If the resulting component value is below 0 or above 255, the component value is clamped to these limits.
Note
The new image is a ResourceVectorImage. The image buffer is allocated in the MicroUI image heap. The application must manage the image cycle life and close the image to free the image buffer.
A VectorImage object can also be drawn associated to a color matrix by a call to ej.microvg.VectorGraphicsPainter.drawFilteredImage().
The following example illustrates this feature.
Animated Vector Images
The Android Vector Drawable format provides the ability to change the properties of vector graphics over time, in order to create animated effects.
The transformations of the objects over the time are embedded in the Vector image file and a call to ej.microvg.VectorGraphicsPainter.drawAnimatedImage() or ej.microvg.VectorGraphicsPainter.drawFilteredAnimatedImage() will draw the image for a specific time frame.
The application can get the duration of the image animation with a call to ej.microvg.VectorImage.getDuration().
Every image object that is animated outside the image viewbox is clipped at the image boundary. In any cases, especially when the image is rotated, the image boundary is the rectangle that contains all the corners of the original image.
The supported file format is an Animated Vector Drawable xml file with animations and vector definition in the same file as described in Android API.
The SVG format also supports the animation of vector graphics objects, but this feature is not yet implemented in the MicroVG library for this file format.
SVG files that need to be animated should be converted to Android Vector Drawable format with the Android Vector Asset tool and then animated manually or with a tool like Shapeshifter.
Warning
A flaw in Eclipse Temurin™ JDK 8 causes animated vector images to render incorrectly on the Simulator. You should upgrade to Eclipse Temurin™ JDK 11 instead.
Supported animations
This section will present the different available animations with an example.
For each example, this simple java code will be used.
VectorImage image = VectorImage.getImage("/images/myImage.xml"); //$NON-NLS-1$
Matrix matrix = new Matrix();
matrix.setTranslate(100,100);
matrix.preScale(2,2);
long elapsed = 0;
long step = 10;
while (true) {
// Clear Screen
g.setColor(Colors.BLACK);
Painter.fillRectangle(g, 0, 0, display.getWidth(), display.getHeight());
VectorGraphicsPainter.drawAnimatedImage(g, image, matrix, elapsed);
display.flush();
// Pause the current thread
try {
Thread.sleep(step);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Update current image time
if (elapsed < image.getDuration()) {
elapsed += step;
} else {
elapsed = 0;
}
}
TranslateX and TranslateY
Any group in the Android Vector Drawable can be translated in X or Y direction with an object animator.
TranslateXY over a path
Any group in the Android Vector Drawable can be translated over a path.
ScaleX and ScaleY
A group in the Android Vector Drawable can be scaled on X or Y direction. The scaling pivot point is the one defined in the group attributes. By default, the pivot point is (0,0).
Rotate
A group in the Android Vector Drawable can be rotated around a pivot point. The pivot point is the one defined in the group attributes. By default, the pivot point is (0,0).
Morphing
The Android Vector Drawable format supports the animation of the pathData attribute of a path. With this type of animation a shape can be transformed to a totally different other shape. The only constraint is that the origin and destination pathData must have the same commands format.
Lets take, for instance, the morphing of a rectangle to a circle which have the following commands.
Circle: M 11.9 9.8 C 11.9 8.1 13.3 6.7 14.9 6.7 C 16.6 6.7 18 8.1 18 9.8 C 18 11.6 16.6 13 14.9 13 C 13.3 13 11.9 11.6 11.9 9.8 Z
Rectangle: M 11.9 6.7 H 18 V 13 H 11.9 Z
The rectangle path has to be reworked to match with the sequence of commands of the circle path.
The following tools can be used to manipulate the paths to create the wanted animation effect:
There is an infinity of possibilities to create the new path, and the association of each points of the paths will induce a specific morphing animation. As an example, let’s define two rectangles very similar visually but with different definitions:
New Rectangle path1: M 11.9 9.8 C 11.897 7.735 11.906 7.995 11.906 6.697 C 16.6 6.7 16.601 6.706 17.995 6.697 C 18 11.6 17.995 11.587 18.004 13.006 C 13.3 13 13.852 13.006 11.897 13.006 Z
New Rectangle path2: M 11.906 6.697 C 11.953 6.698 12.993 6.698 17.995 6.697 C 17.999 8.331 17.997 9.93 18.002 13.004 C 16.239 13.007 16.009 13.001 11.893 13.007 C 13.3 13 13.852 13.006 11.893 13.007 Z
Warning
As path strokes are converted at build-time to filled path, the morphing of stroked paths is not supported. Any image with a path morphing animation on a stroked path will be rejected. Path strokes must be manually converted to filled path and the morphing of these new filled paths must be created.
Color and Opacity
Any path fillColor, strokeColor, fillAlpha and strokeAlpha attributes in the Android Vector Drawable can be animated.
Warning
The color of paths colored with a linear gradient can not be animated.
Easing Interpolators
Every animation is associated with an easing interpolator. By default, the animation transition is linear, but the rate of change in the animation can be defined by an interpolator. This allows the existing animation effects to be accelerated, decelerated, repeated, bounced, etc.
The supported Android interpolators are:
accelerate_cubic
accelerate_decelerate
accelerate_quad
anticipate
anticipate_overshoot
bounce
cycle
decelerate_cubic
decelerate_quad
decelerate_quint
fast_out_extra_slow_in
fast_out_linear_in
fast_out_slow_in
linear
linear_out_slow_in
overshoot
Any other vectorial path can also be used as the interpolator easing function.
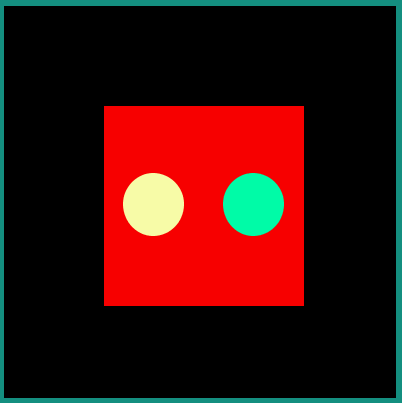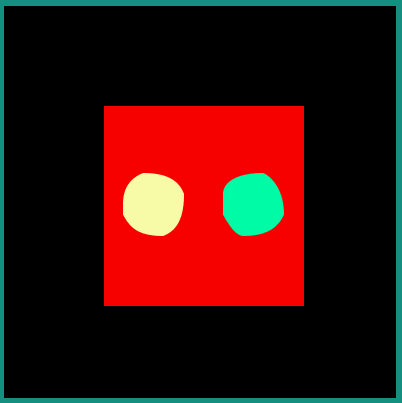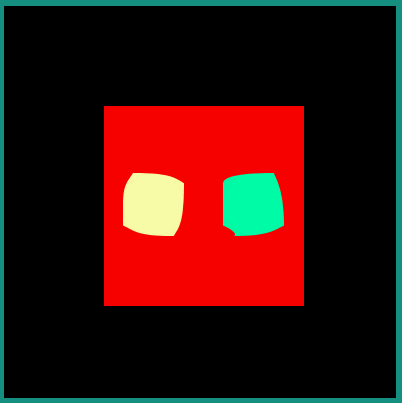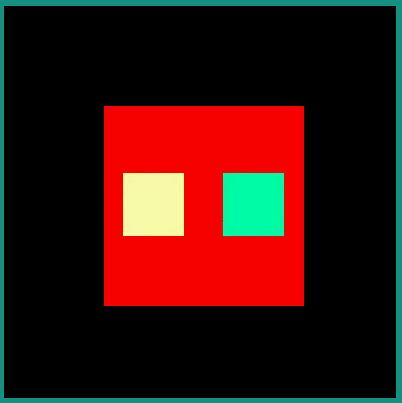
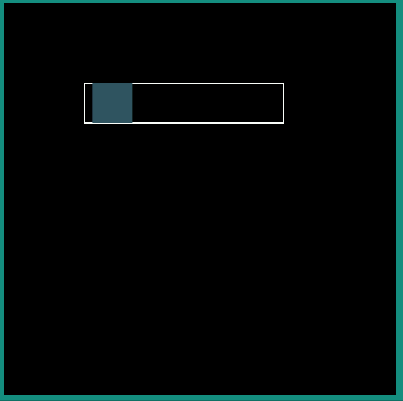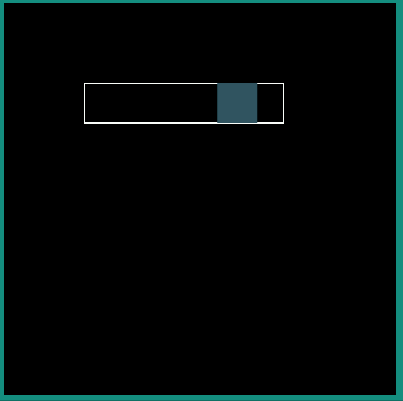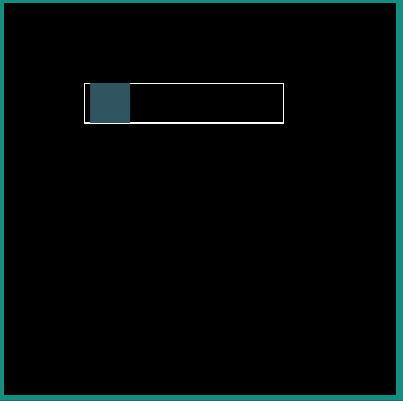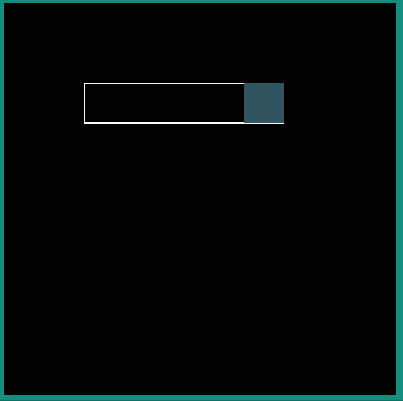
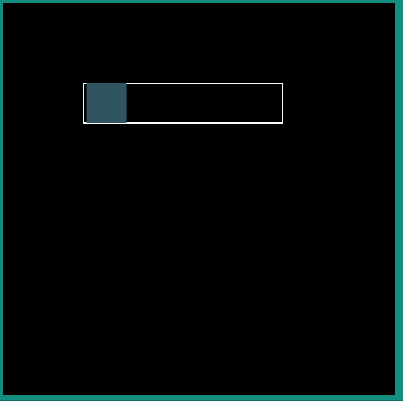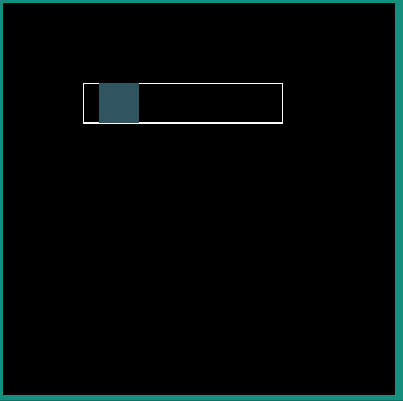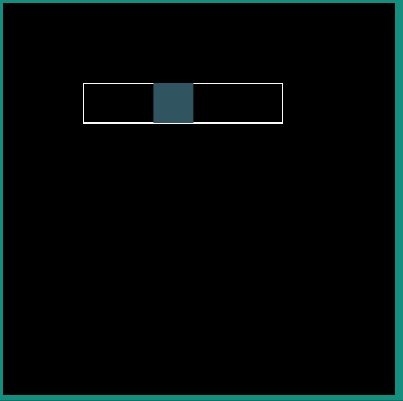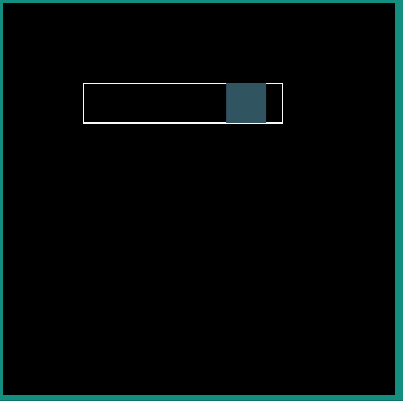
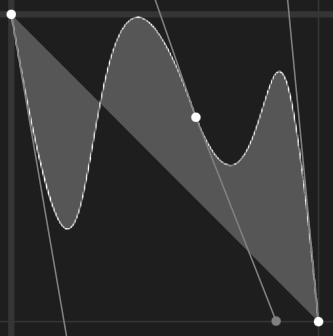
Following examples show the behavior of some of the interpolators for a simple translation animation.
Image:
<animated-vector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:aapt="http://schemas.android.com/aapt">
<aapt:attr name="android:drawable">
<vector android:width="100dp" android:height="100dp" android:viewportWidth="100" android:viewportHeight="100">
<path android:pathData="M 0 0 h100 v20 h-100 Z" android:strokeColor="#FFFFFF" android:strokeWidth="1"/>
<group android:name="translate">
<path android:pathData="M 0 0 h20 v20 h-20 Z" android:fillColor="#335566"/>
</group>
</vector>
</aapt:attr>
<target android:name="translate">
<aapt:attr name="android:animation">
<set><objectAnimator
android:propertyName="translateX"
android:duration="2000"
android:valueFrom="0"
android:valueTo="80"
android:interpolator = "@android:interpolator/linear" />
</set>
</aapt:attr>
</target>
</animated-vector>
android:interpolator = "@android:interpolator/linear"
|
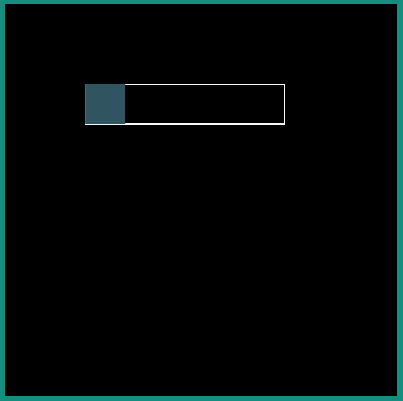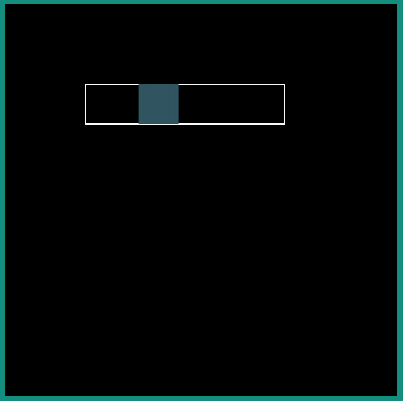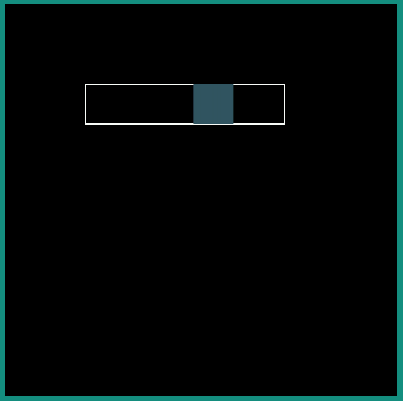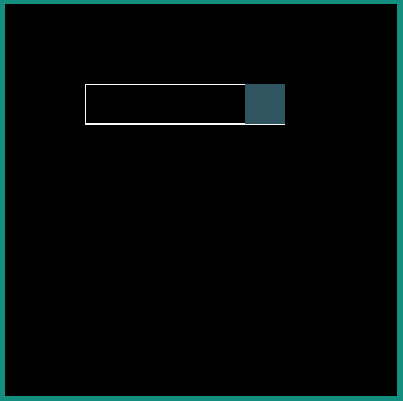
|
android:interpolator = "@android:interpolator/accelerate_cubic"
|
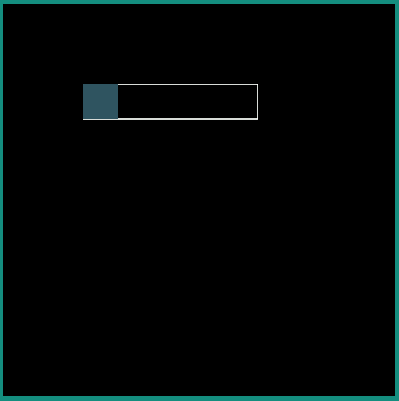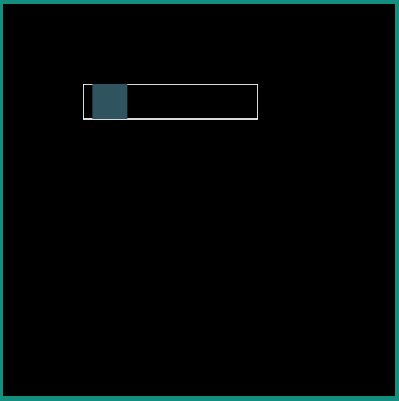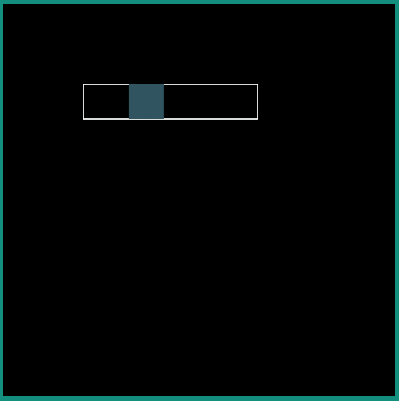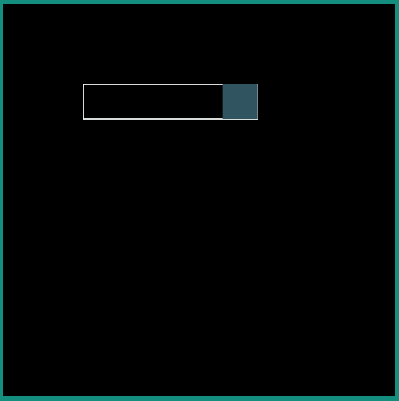
|
android:interpolator = "@android:interpolator/bounce"
|
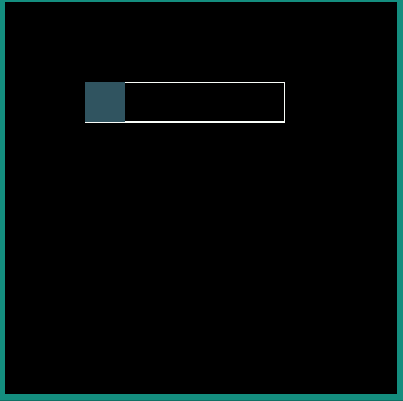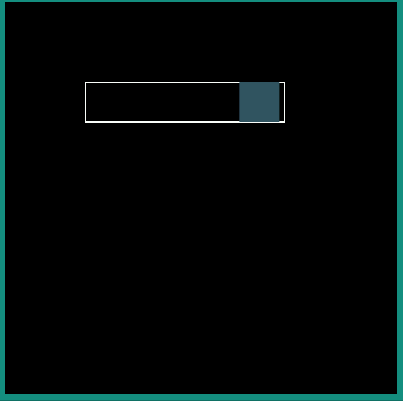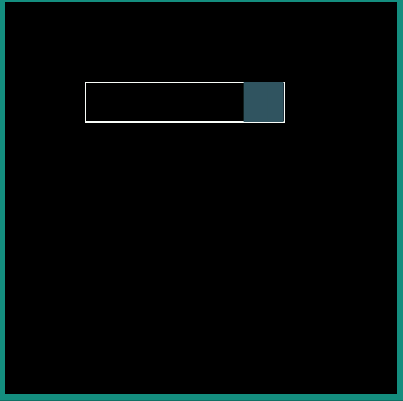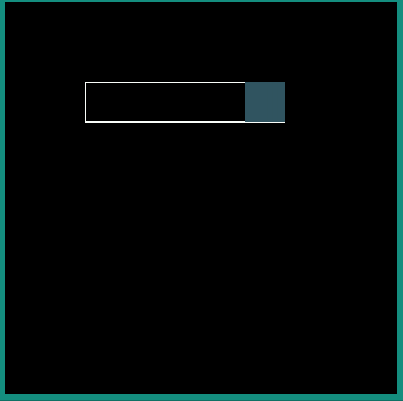
|
android:interpolator = "@android:interpolator/fast_out_slow_in"
|
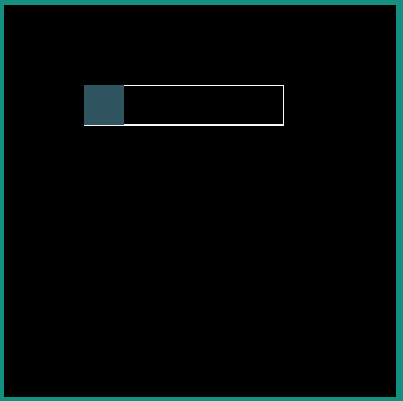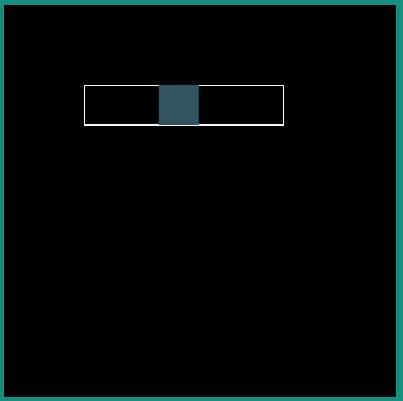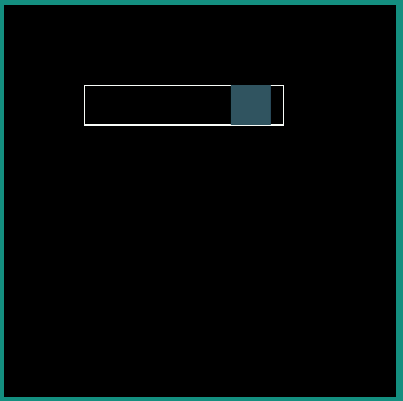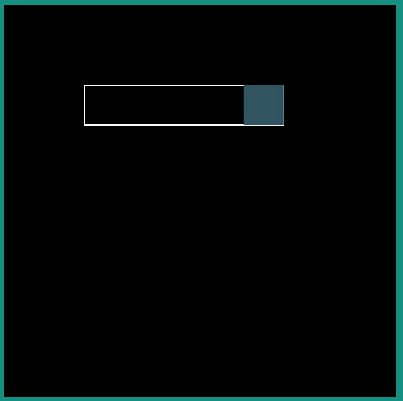
|
<aapt:attr name="android:interpolator">
<pathInterpolator android:pathData="M 0 0 C 0.371 2.888 0.492 -1.91 1 1"/>
</aapt:attr>
|
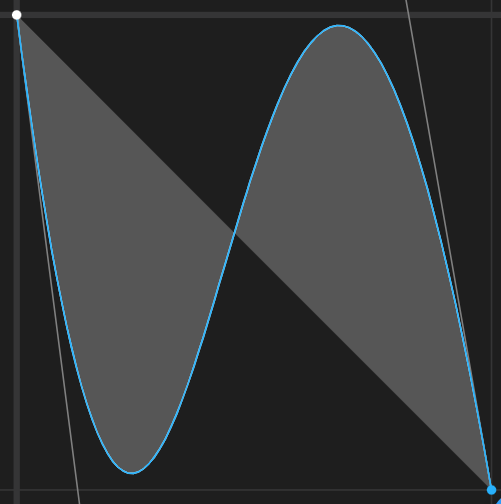
|
<aapt:attr name="android:interpolator">
<pathInterpolator android:pathData="M 0 0 C 0.333 1.939 0.171 -0.906 0.601 0.335 C 0.862 0.998 0.83 -0.771 1 1"/>
</aapt:attr>
|
|
External Images
To fetch images from external memory, the application must pre-register the external Image resources. The management of this kind of image may be different than the compile-time images and may require some allocations in the MicroUI Images Heap. For more details about the external image management, refers to the VEE Port Guide chapter External Memory.
Caching Generated Images
Images converted using the Image Generator can be cached so that they are not rebuilt every time the application is launched. Doing so can significantly speed up the application build phase.
See Caching Generated Images to have more details.
Note
The cache is available from version 13.6 of the UI Pack.
Limitations / Supported Features
Android Vector Drawable
The MicroVG library supports most of the Android Vector Drawable features with the following limitations:
clip-pathfeature is only supported for static images.trim-pathanimation is not supported.morphing animations are not supported for paths with stroke.
usage of path opacity is limited
drawImagewith alpha is not supported if the image contains overlapping paths.images with global alpha(
android:alphaattribute ofvectorelement) and overlapping paths are not supported.Beware that using
android:fillColorandandroid:strokeColorattributes on the same path leads to overlapping paths.
radialandsweepgradient types are not supported.tint,tintModeandautoMirroredfeatures are not supported.trimPathfeature is not supported.
SVG
The MicroVG library supports a subset of SVGTiny: https://www.w3.org/TR/SVGTiny12/ including:
Path
Basic shape
Painting filling
Painting stroking
Painting gradient (only linear gradient with one pattern)
Painting color formats : #RRGGBB, #RGB, rgb(r,g,b), keywords
Transforms
Text
Fonts (the text fonts used in the SVG file has to be installed on the operating system)