Resource Manager
The Resource Manager is a software component of the KF-Util library. It allows the kernel to apply a set of controls, defined in a policy file, to a feature. A control denotes either a resource limit (CPU, RAM, flash storage, network bandwidth) or the feature’s priority level.
Principle
When a feature is installed, the kernel checks whether it embeds a policy file. A policy file is a description file formatted in JSON. If present, the policy file is loaded and its rules are enforced throughout the lifecycle of the feature. It is assumed that the policy file has been approved beforehand by a moderator.
The behaviour of each control is described as follows:
Priority: Sets the priority of the threads owned by the feature.
CPU: When a feature has reached its CPU quota, it is suspended until all other features consume their own quotas.
RAM: If a feature exceeds its RAM limit, an
OutOfMemoryErroris raised and the feature is stopped and uninstalled. For more information about RAM control, please refer to this section.Flash storage: If the flash storage limit is exceeded, a
StorageLimitExceptionis thrown.Network bandwidth: Exceeding the daily bandwidth limit on the specified subnet triggers a
BandwidthLimitException.
The following diagram illustrates a simplified flow of the Resource Manager.
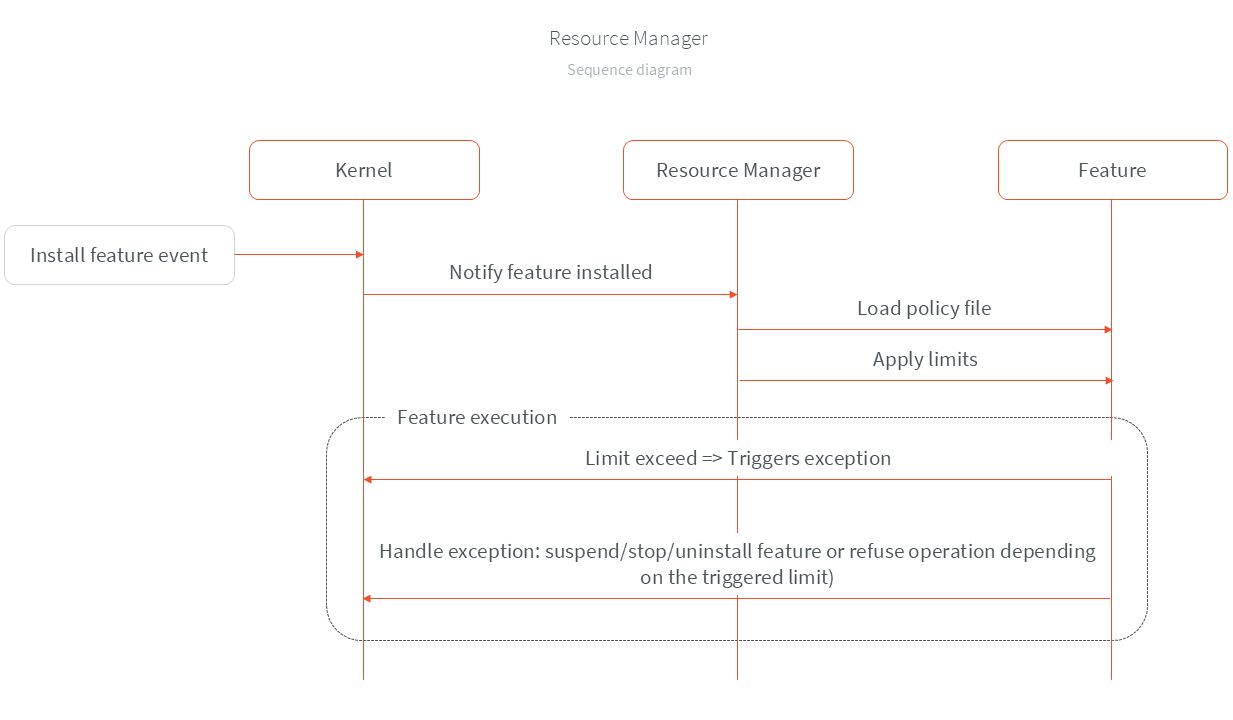
Policy File Format
To define a policy, a feature must include a policy file as a resource. By default, the resource name is set to /feature.policy.json.
This filename can be overridden in the kernel configuration via a system property, as shown below:
# Feature policy file
feature.policy.name=/feature.policy.json
The policy file is provided in JSON format. An example is shown below:
{
"priority": 5,
"resources": {
"limit": {
"cpu": 30,
"ram": 6400,
"flash": 1024
}
},
"networkData": {
"upstream": [
{
"dailyDataLimit": 1024,
"cidrSubnet": "127.0.0.1/24"
}
]
}
}
Attributes
priority: Acceptable values for the priority level range from 1 to 10.
cpu: CPU usage limit expressed as a percentage (relative to a calibrated 100% baseline).
ram: RAM allocation limit expressed in bytes.
flash: Flash memory limit expressed in bytes. Flash storage operations are done over FS. Please refer to StorageFs for details.
- networkData:
cidrSubnet: Allowed IP range in CIDR notation.
dailyDataLimit: Daily upstream limit expressed in bytes.
Kernel Implementation
Here are the steps to integrate the Resource Manager in your kernel:
Add the KF-Util library dependency in the kernel build file.
implementation("com.microej.library.util:kf-util:3.1.0")<dependency org="com.microej.library.util" name="kf-util" rev="3.1.0"/>
Create an instance of the Resource Manager.
FeaturePolicyEnforcer policyEnforcer = new FeaturePolicyEnforcer();
Apply the policy when a feature is installed in the
stateChanged(Feature feature, @Nullable Feature.State previousState)method of your FeatureStateListener implementation.
public class CustomFeatureStateListener implements FeatureStateListener {
@Override
public void stateChanged(Feature feature, @Nullable State previousState) {
switch (feature.getState()) {
case INSTALLED:
if (previousState == null) {
try {
// The policyEnforcer instance is already created.
policyEnforcer.applyPolicy(feature);
} catch (Exception exception) {
// Log or handle exception.
}
}
break;
// Other states.
default:
break;
}
}
}
Note
Steps 2 and 3 are already implemented within the SandboxedModuleManager and ApplicationModule wrappers provided by the KF-Util library. If you’re using these wrappers, no additional code is required.
