Warning
This documentation is for SDK 5. The latest major version is SDK 6. SDK 5 is in maintenance mode since the release of SDK 5.8.0. Consequently, as stated in the SDK End User License Agreement (EULA), the SDK will reach the end of its life by July 2028. Contact our support team for assistance with migrating to the new SDK, or your sales representative if you require an extension of SDK maintenance as a service.
Create a VEE Port
This section describes the steps to create a new VEE Port with the SDK, and options to connect it to an external Board Support Package (BSP) as well as a third-party C toolchain.
Note
The creation of a VEE Port with this guide requires at least the version 5.4.0 of the SDK.
Note
If you own a legacy VEE Port, you can either create your VEE Port again from scratch, or follow the Former Platform Migration chapter.
VEE Port Project Creation
The first step is to create a VEE Port configuration project:
Select File > New > Project… > General > Project,
Enter a Project name. The name is arbitrary and can be changed later. The usual convention is
[PLATFORM_NAME]-configuration,Click on Finish button. A new empty project is created,
Install the latest Platform Configuration Additions by following instructions described at https://github.com/MicroEJ/VEEPortQualificationTools/blob/master/framework/platform/README.rst.
Files within the
content-sdk-5folder must be copied to the configuration project folder.Files within the
content-architecture-7must be copied to the configuration project folder only if you are using an Architecture version7.x. If you are using an Architecture version8.x, the files are already included and must not be copied.
You should get a MicroEJ Platform configuration project that looks like:
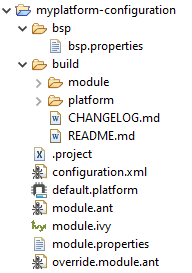
MicroEJ Platform Configuration Project Skeleton
Note
The version of installed Platform Configuration Additions is indicated in the CHANGELOG file.
Architecture Selection
The next step is to select a MicroEJ Architecture compatible with your device instructions set and C compiler.
MicroEJ Corp. provides MicroEJ Evaluation Architectures for most common instructions sets and compilers at https://repository.microej.com/modules/com/microej/architecture.
Please refer to the chapter Architectures MCU / Compiler for the details of ABI and compiler options.
If the requested MicroEJ Architecture is not available for evaluation or to get a MicroEJ Production Architecture, please contact your MicroEJ sales representative or our support team.
Once you know which Architecture to use, add it as a dependency of the VEE Port configuration project as described below:
Edit the Module Description File
module.ivyto declare the MicroEJ Architecture dependency:<dependencies> <dependency org="com.microej.architecture.[ISA].[TOOLCHAIN]" name="[UID]" rev="[VERSION]"> <artifact name="[UID]" m:classifier="[USAGE]" ext="xpf"/> </dependency> </dependencies>
The name of the module dependency needed for your Platform can be found in the chapter Architectures MCU / Compiler. Check the table of your corresponding Architecture and follow the link in the Module column.
For example, to declare the MicroEJ Evaluation Architecture version
7.14.0for Arm® Cortex®-M4 microcontrollers compiled with GNU CC toolchain:<dependencies> <dependency org="com.microej.architecture.CM4.CM4hardfp_GCC48" name="flopi4G25" rev="7.14.0"> <artifact name="flopi4G25" m:classifier="eval" ext="xpf"/> </dependency> </dependencies>
And the module for this Architecture is located in the Central Repository at https://repository.microej.com/modules/com/microej/architecture/CM4/CM4hardfp_GCC48/flopi4G25/7.14.0/.
Note
The Platform Configuration Additions allow to select the Architecture
USAGEusing the optioncom.microej.platformbuilder.architecture.usage. Edit the filemodule.propertiesto set the property toprodto use a Production Architecture and toevalto use an Evaluation Architecture.
Pack Import
MicroEJ Pack provides additional features on top of the MicroEJ Architecture such as Graphical User Interface or Networking.
Note
MicroEJ Packs are optional. You can skip this section if you intend to integrate MicroEJ runtime only with custom libraries.
To add a MicroEJ Pack, add it as a dependency of the VEE Port configuration project as described below:
Edit the Module Description File
module.ivyas follows:<dependencies> <!-- MicroEJ Architecture Specific Pack --> <dependency org="com.microej.architecture.[ISA].[TOOLCHAIN]" name="[UID]-[NAME]-pack" rev="[VERSION]"/> <!-- MicroEJ Generic Pack --> <dependency org="com.microej.pack.[NAME]" name="[NAME]-pack" rev="[VERSION]"/> <!-- Legacy MicroEJ Generic Pack --> <dependency org="com.microej.pack" name="[NAME]" rev="[VERSION]"/> </dependencies>
For example, to declare the MicroEJ Architecture Specific Pack UI version 13.0.4 for MicroEJ Architecture
flopi4G25on Arm® Cortex®-M4 microcontrollers compiled with GNU CC toolchain:<dependencies> <!-- MicroEJ Architecture Specific Pack --> <dependency org="com.microej.architecture.CM4.CM4hardfp_GCC48" name="flopi4G25-ui-pack" rev="13.0.4"/> </dependencies>
To declare the MicroEJ Generic Pack Bluetooth version 2.1.0:
<dependencies> <!-- MicroEJ Generic Pack --> <dependency org="com.microej.pack.bluetooth" name="bluetooth-pack" rev="2.1.0"/> </dependencies>
And to declare the Legacy MicroEJ Generic Pack Net version 9.2.3:
<dependencies> <!-- Legacy MicroEJ Generic Pack --> <dependency org="com.microej.pack" name="net" rev="9.2.3"/> </dependencies>
Warning
MicroEJ Architecture Specific Packs and Legacy MicroEJ Generic Packs provide Platform modules that are not installed by default. See Platform Module Configuration section for more details.
VEE Port Build
The VEE Port can be built either from the SDK or from the MMM CLI. To build the VEE Port from the SDK, perform a regular Module Build:
Right-click on the VEE Port Configuration project,
Select Build Module.
To build the VEE Port from the MMM CLI:
Set the
eclipse.homeproperty to the path of your SDK, using-Declipse.home=<path>in the command line or using the Shared configuration.By default, the SDK’s path is one of the following directories:
on Windows:
C:\Program Files\MicroEJ\MicroEJ-SDK-<YY.MM>\rcpon Linux:
/home/<user>/MicroEJ/MicroEJ-SDK-<YY.MM>/rcpon macOS:
/Applications/MicroEJ/MicroEJ-SDK-<YY.MM>/rcp/MicroEJ-SDK-<YY.MM>.app/Contents/EclipseFrom the VEE Port Configuration project, execute the command:
mmm
In both cases, the build starts and the build logs are redirected to the integrated console. Once the build is terminated, you should get the following message:
module-platform:report: [echo] ============================================================================================================ [echo] Platform has been built in this directory 'C:\tmp\mydevice-Platform-[TOOLCHAIN]-0.1.0'. [echo] To import this project in your MicroEJ SDK workspace (if not already available): [echo] - Select 'File' > 'Import...' > 'General' > 'Existing Projects into Workspace' > 'Next' [echo] - Check 'Select root directory' and browse 'C:\tmp\mydevice-Platform-[TOOLCHAIN]-0.1.0' > 'Finish' [echo] ============================================================================================================ BUILD SUCCESSFUL Total time: 43 seconds
Then, import the VEE Port directory to your SDK workspace as mentioned in the report. You should get a ready-to-use VEE Port project in the workspace available for the MicroEJ Application project to run on. You can also check the VEE Port availability in: Window > Preferences > MicroEJ > Platforms in workspace.
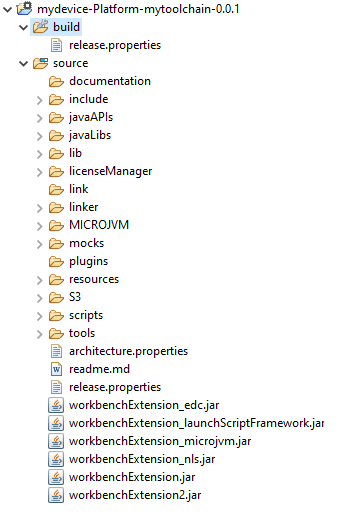
VEE Port Project
This step is only required the first time the VEE Port is built, or if the VEE Port properties have changed (i.e, name, version). When the same VEE Port is built again, the Platform project should be automatically refreshed after a few seconds. In case of any doubt, right-click on the VEE Port project and select Refresh to get the new content.
Platform Module Configuration
The primary mechanism for augmenting the capabilities of a Platform is to add modules to it.
A MicroEJ module is a group of related files (Foundation Libraries, scripts, link files, C libraries, Simulator Mock, tools, etc.) that together provide all or part of a Platform capability.
A module can extend a Architecture with additional features such as:
Runtime Capability (e.g. Multi-Sandbox, External Resources Loader) ,
Simulator (e.g. Front Panel Mock),
Tool (e.g. MicroEJ Java H).
VEE Port modules provided by MicroEJ Generic Packs are automatically installed during the VEE Port build and do not require extra configuration. They are not displayed in the VEE Port Editor.
VEE Port modules provided by MicroEJ Architectures, MicroEJ Architecture Specific Packs and Legacy MicroEJ Generic Packs are not installed by default. They must be enabled and configured using the VEE Port Editor.
Before opening the VEE Port Editor, the VEE Port must have been built once to let MicroEJ Module Manager resolve and download MicroEJ Architecture and Packs locally. Then import them in the SDK as follows:
Select File > Import > MicroEJ > Architectures,
Browse myplatform-configuration/target~/dependencies folder (contains
.xpfand.xpfpfiles once the VEE Port is built),Check the I agree and accept the above terms and conditions… box to accept the license,
Click on Finish button. This may take some time.
Once imported, double-click on the default.platform file to open the VEE Port Editor.
From the VEE Port Editor, select the Content tab to access the modules selection. VEE Port modules can be selected/deselected from the Modules frame.
VEE Port modules are organized in groups. When a group is selected, by default all its modules are selected. To view all the modules making up a group, click on the Expand All icon on the top-right of the frame. This will let you select/deselect on a per-module basis. Note that individual module selection is not recommended and that it is only available when the module has been imported.
The description and contents of an item (group or module) are displayed next to the list when an item is selected.
All the selected VEE Port modules will be installed in the VEE Port.
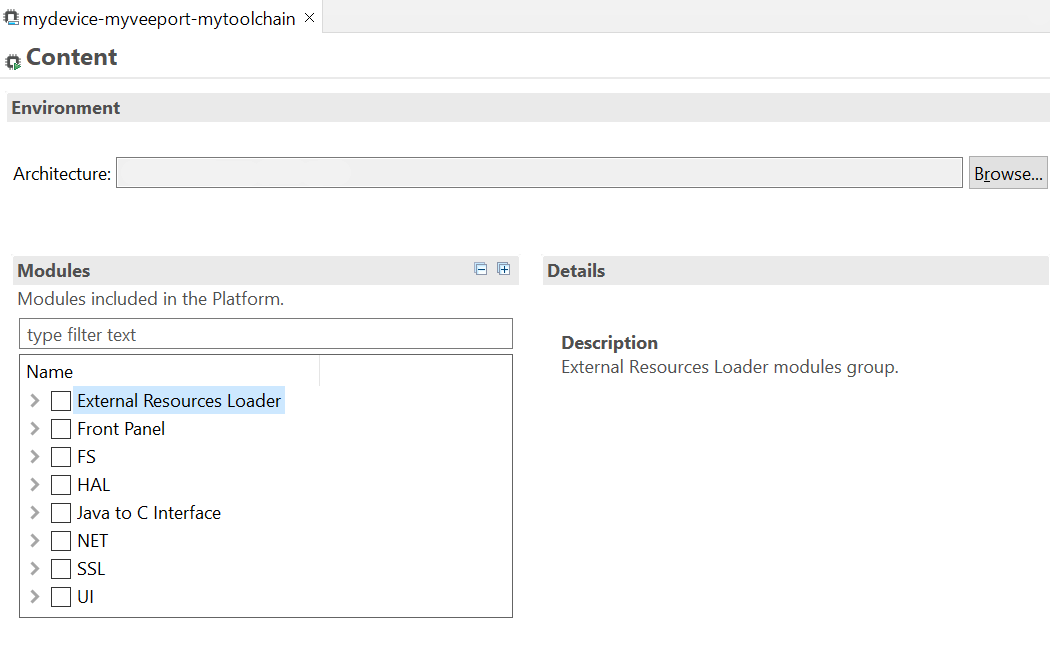
VEE Port Configuration Modules Selection
Each selected VEE Port module can be customized by creating a [module] folder (named after the module name), next to the .platform file definition. It may contain:
A [module].properties file named after the module name. These properties will be injected in the execution context prefixed by the module name. Some properties might be needed for the configuration of some modules. Please refer to the modules documentation for more information.
A bsp.xml file which provides additional information about the BSP implementation of Low Level APIs.
This file must start with the node
<bsp>. It can contain several lines like this one:<nativeName="A_LLAPI_NAME" nativeImplementation name="AN_IMPLEMENTATION_NAME"/>where:
A_LLAPI_NAMErefers to a Low Level API native name. It isspecific to the MicroEJ C library which provides the Low Level API.
AN_IMPLEMENTATION_NAMErefers to the implementation name of theLow Level API. It is specific to the BSP; and more specifically, to the C file which does the link between the MicroEJ C library and the C driver.
These files will be converted into an internal format during the MicroEJ Platform build.
Optional module specific files and folders
Modifying one of these files requires to build the Platform again.
Note
It is possible to quickly rebuild the Platform from the Platform Editor if only the Platform module configuration has changed. Click on the Build Platform link on the Overview tab of the Platform Editor.
VEE Port Customization
The VEE Port configuration project can contain an optional dropins folder. The full content of this folder will be copied in the VEE Port during the build. This feature allows to add or overwrite libraries, tools, etc. into the VEE Port.
The dropins folder organization should respect the PlatVEE Portform files and folders organization. For instance, the tools are located in the sub-folder tools. Launch a VEE Port build without the dropins folder to see how the VEE Port files and folders are organized. Then fill the dropins folder with additional features and build again the VEE Port to get a customized VEE Port.
Files in the dropins folder have priority. If one file has the same path and name as a file already installed in the VEE Port, the file from the dropins folder will be selected first.
The VEE Port build can also be customized by updating the configuration.xml file next to the .platform file. This Ant script can extend one or several of the extension points available. By default, you should not have to change the default configuration script.
Modifying one of these files requires to build the Platform again.
VEE Port Publication
The publication of the built VEE Port to a module repository is disabled by default.
It can be enabled by setting the skip.publish property to false in the module.properties file of
the VEE Port configuration project .
The publication is kept disabled by default in the project sources because developers usually use the locally built VEE Port in the workspace.
However, the publication is required in a Continuous Integration environment.
This can be done by leaving the skip.publish property to true in the project sources
and by overwriting it in the command launched by the Continuous Integration environment, for example:
mmm publish shared -Dskip.publish=false
If the VEE Port is configured with Full BSP connection, the build script can be launched
to validate that the BSP successfully compiles and links before the VEE Port is published.
It can be enabled by setting the com.microej.platformbuilder.bsp.build.enabled property to true
in the module.properties file of the VEE Port configuration project (defaults to false if not set).
BSP Connection
In order to build the Executable of an Application, the BSP Connection must be configured. Refer to the BSP Connection section for more details.
Platform API Documentation
The Platform API documentation provides a comprehensive HTML Javadoc that combines all the Foundation Library APIs.
It can be built using the following steps:
Create a new module repository project.
Enable module repository javadoc generation (see Generate Javadoc).
Go to your Platform build directory and browse
source/javaLibsandsource/MICROJVM/javaLibsdirectories. You will find Foundation Libraries implementations JAR files in the following pattern:<module_name>-<major>.<minor>.jar.Example:
EDC-1.3.jar:module_name=edc,major=1,minor=3.For each Foundation Library your want to include,
Retrieve its api module in either the Central Repository, Developer Repository or your custom repository. Most of the Foundation Library APIs provided by MicroEJ are available under the
ej.apiorganization.Example: EDC is on the Central Repository (https://repository.microej.com/modules/ej/api/edc/)
Get the latest available patch version corresponding to your
<major>.<minor>version. This allows to benefit from the latest javadoc fixes and updates for the corresponding version.Example:
ej.api#edc#1.3.5:patch``=``5Declare a dependency line in the module repository.
<dependency conf="artifacts->*" transitive="false" org="<org>" name="<module_name>" rev="<major>.<minor>.<patch>" />
Example:
<dependency conf="artifacts->*" transitive="false" org="ej.api" name="edc" rev="1.3.5" />
Build the module repository.
The Platform API documentation is available in <module_repository_project>/target~/artifacts/<module_repository_name>-javadoc.zip.
Link-Time Option
It is possible to define custom Application options that can be passed to the BSP through an ELF symbol defined at link-time, hence the term link-time option. This allows to provide configuration options to the Application developer without the need to rebuild the BSP source code.
To define a link-time option, first choose an option name with only alphanumeric characters ([a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z0-9]* without spaces).
Proceed with the following steps by replacing [my_option] with your option name everywhere:
Create a folder inside your VEE Port Customization part (e.g:
[platform]-configuration/dropins/scripts/init-[my_option])Create an init script file and put it inside (e.g:
[platform]-configuration/dropins/scripts/init-[my_option]/init-[my_option].xmlfile). Here is the init script file template content:<project name="[my_option]-init"> <target name="init/execution/[my_option]" extensionOf="init/execution" if="onBoard"> <!-- Set option default value --> <property name="[my_option]" value="0"/> <!-- Create tmp dir --> <local name="link.files.dir"/> <microejtempfile deleteonexit="true" prefix="link[my_option]" property="link.files.dir"/> <mkdir dir="${link.files.dir}"/> <!-- Get tmp link file name --> <local name="link.[my_option]"/> <property name="link.[my_option]" value="${link.files.dir}/[my_option].lscf" /> <echoxml file="${link.[my_option]}" append="false"> <lscFragment> <defSymbol name="[my_option]" value="${[my_option]}" rootSymbol="true"/> </lscFragment> </echoxml> <!-- Add link file in linker's link files path --> <augment id="partialLink.lscf.path"> <path location="${link.files.dir}"/> <path location="${jpf.dir}/link"/> </augment> </target> </project>
In your BSP source code, define an ELF symbol
[my_option]can then be used inside C files in your BSP with:// Declare the symbol as an extern global extern int [my_option]; void my_func(void){ // Get the symbol value int [my_option]_value = ((int)(&[my_option])); // Get the symbol value if([my_option]_value == 1){ ... } else{ ... } }
Warning
A Link-time option should avoid to be set to 0.
Some third-party linkers consider such symbols as undefined, even if they are declared.
