Introduction
A MicroEJ Architecture is a software package that includes the MicroEJ Runtime port to a specific target Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) and C compiler. It contains a set of libraries, tools and C header files.
A VEE Port is a MicroEJ Architecture port for a custom device.
It relies on C drivers (a.k.a. low level LL drivers) for each VEE Port feature.
These drivers are implemented in the VEE Port BSP project. This project is edited in the C compiler IDE/dev environment (e.g. KEIL, GCC, IAR).
For example, the MicroUI library LED feature will require a LLUI_LED.c that implements the native on/off IO drive.
Each VEE Port is specific to:
a MicroEJ Architecture (MCU ISA and C compiler)
an optional RTOS (e.g. FreeRTOS - note: the MicroEJ Runtime can run bare metal)
a device: the OS bring up code that is device-specific (e.g. the MCU specific code/IO/RAM/Clock/Middleware… configurations)
MicroEJ Corp. provides MicroEJ Evaluation Architectures at https://repository.microej.com/modules/com/microej/architecture, and VEE Port Examples for various evaluation boards.
The VEE Porting Guide explains how the core features are accessed, configured and used to create a port of MICROEJ VEE (VEE Port) on your dedicated device. It also explains how an Application interacts with native code, and the details of the Architecture modules, including their APIs, error codes and options.
Semantics of implemented Foundation Libraries are described in their respective chapters as well as the required Abstraction Layers APIs for porting them to different targets.
VEE Port Build Process
The following figure shows the overall process to create an Executable file to deploy on a device. The first three steps are performed within MICROEJ SDK. The remaining steps are performed within the C IDE.
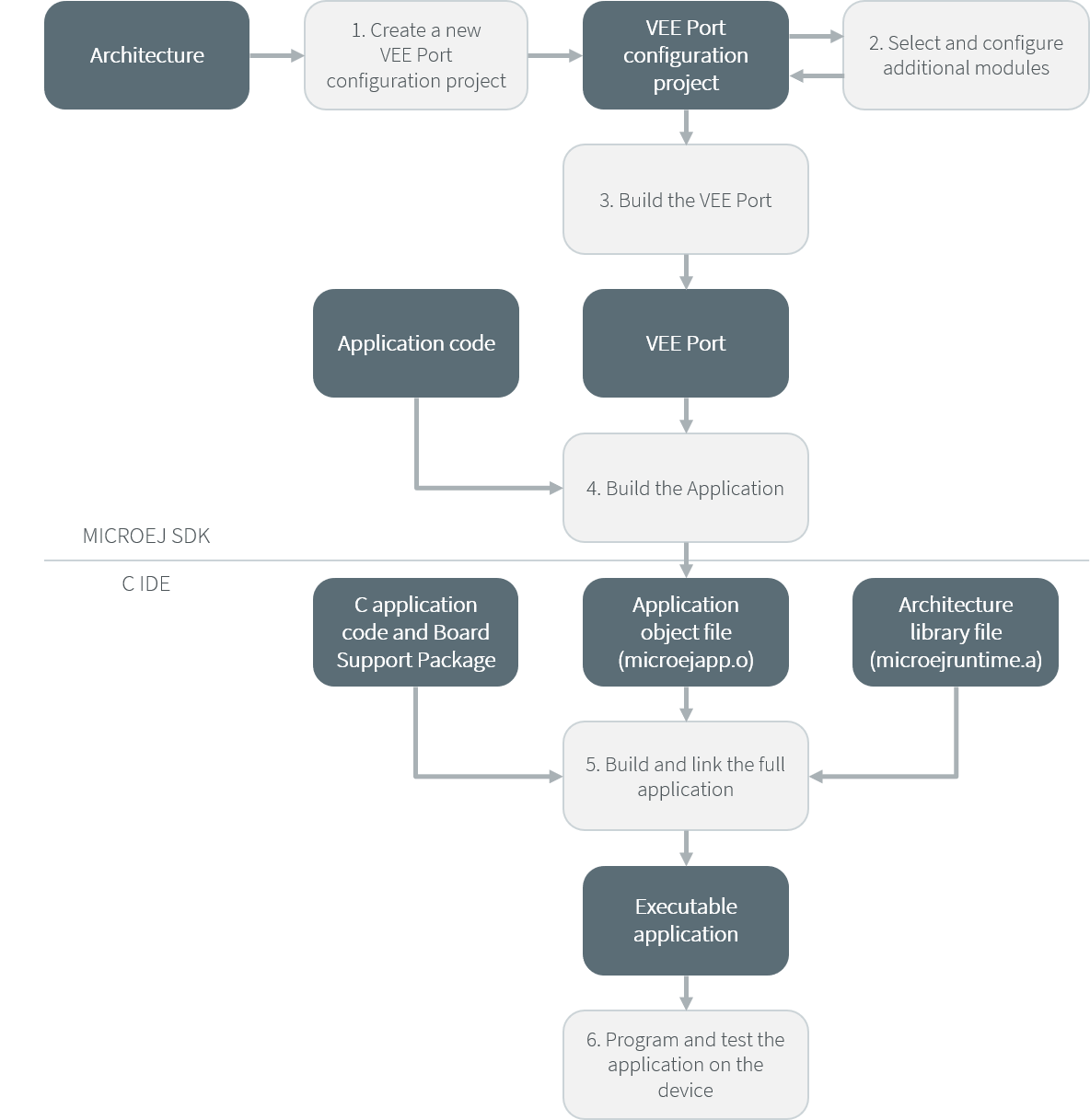
Overall Build Process
The steps are as follow:
Create a new VEE Port configuration project. This project describes the VEE Port to build (Architecture selection).
Select which modules provided by the Architecture and Packs will be installed in the VEE Port.
Build the VEE Port according to the choices made in steps 1 and 2.
Build an Application against the VEE Port in order to obtain an object file to link in the BSP.
Compile the BSP and link it with the Application object file that was built previously in step 4 to produce an Executable.
Final step: Deploy the Executable (i.e. the binary application) onto a device.
Create a VEE Port for a Custom Device
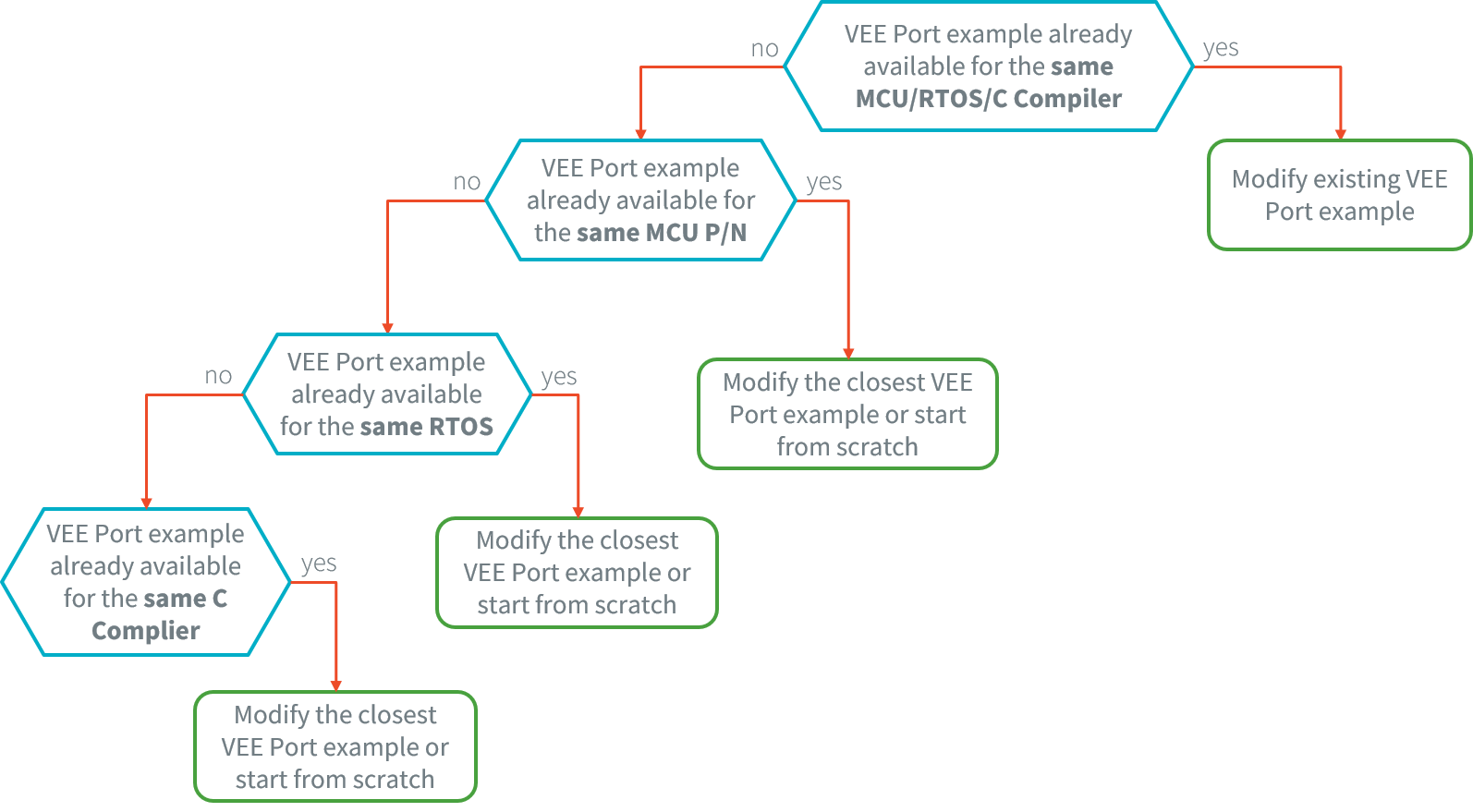
VEE Port creation can either be done from scratch or modifying an existing VEE Port example project. The following chart provides a handy guide to ease decision:
Before going on, make sure that the new device hardware is validated and at least a trace output is available. It is also a good idea to run basic hardware tests like:
Internal and external flash programming and verification
RAM 8/16/32 -bit read/write operations (internal and external if any)
EEMBC Coremark benchmark to verify the CPU/buses/memory/compiler configuration
A VEE Port Example is already available for the same MCU/RTOS/C Compiler
This is the fastest way: VEE Port Examples are usually provided for a silicon vendor evaluation board. Use this VEE Port project and adapt it to your needs.
As the MCU, RTOS and compiler are the same, only the device-specific code needs to be changed (external RAM, external oscillator, communication interfaces).
VEE Port Configuration
Modify the VEE Port project to match the device features and its associated configuration (e.g. GUI, Networking, …).
Refer to VEE Port configuration documentation for SDK 6 or SDK 5 to learn more about it.
More details on available modules can be found in the VEE Porting Guide.
BSP
Required actions:
Modify the BSP C project to match the device specification:
Edit the scatter file/link options.
Edit the compilation options.
Create/review/change the platform Low Level C drivers. They must match the device components and the MCU IO pin assignment:
Note
A number of
LL*.hfiles are referenced from the project. Implement the function prototypes declared there so that the Core Engine can delegate the relevant operations to the provided BSP C functions.
Simulator
Modify the existing Simulator Front Panel project.
A VEE Port Example is not available for the same MCU/RTOS/C Compiler
Look for an available VEE Port Example that will match in order of priority:
same MCU part number
same RTOS
same C compiler
At this point, consider either to modify the closest VEE Port:
Modify the VEE Port configuration.
in the C IDE, start from an empty project that matches with the MCU.
Or to start from scratch a new VEE Port:
Create the VEE Port project and refer to the selected VEE Port as a model for implementation (refer to the VEE Port Creation documentation for SDK 6 or SDK 5).
In the C IDE, start from an empty project and implement the drivers of each of the LL drivers API.
Make sure to link with:
The
microejruntime.athat runs the Core Engine for a specific MCU Architecture.The
microejapp.othat contains the compiled Java application.
MCU
The MCU specific code can be found:
in the C project IDE properties
in the linker file
the IO configuration
in the low level driver (these drivers are usually provided by the silicon vendor)
RTOS
The LL driver is named LLMJVM_[RTOS].c/.h. Modify this file to match the selected RTOS.
C Compiler
The BSP project is provided for a specific compiler (that matches the selected platform architecture).
Start a new project with the compiler IDE that includes the LL drivers and start the VEE Port in the main() function.
Platform Validation
Refer to VEE Port Qualification to qualify the VEE Port.
Further Assistance Needed
Please note that porting MicroEJ to a new device is also something that is part of our engineering services. Consider contacting our sales team to request a quote.